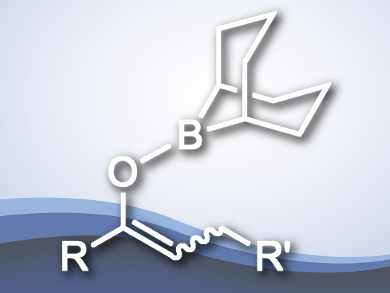
The functionalization of carbonyl compounds is important in organic synthesis. One approach for this is forming a C–C double bond at the α or β positions. Several methods exist for forming such double bonds, including dehydrogenation, dehydrohalogenation, dehydrosulfonation, and oxidation with o-iodoxybenzoic acid. The palladium-catalyzed dehydrosilylation of carbonyl-derived silyl enolates has recently been added to this range of syntheses.
Toshikazu Hirao and colleagues, Osaka University, Japan, have developed a Pd(II)-catalyzed dehydroboration of boron enolates, which are derived from carbonyl compounds and iodo-9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan, to produce α,β-unsaturated ketones. Employing a catalytic amount of PdCl2(PhCN)2 with Cu(OAc)2 at room temperature transformed the enolates into the corresponding trans-selective ketone products in high yields.
Using 1H NMR spectroscopy, this reaction was found to be faster than the analogous process with silyl enolates. Notably, the presence of Pd did not interfere with bromide and chloride substituents on the aryl ring; these remained intact during the reaction. The reaction has a versatile substrate scope and is expected to have a range of applications.
- Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Dehydroboration via Generation of Boron Enolates,
Yuki Sakamoto, Toru Amaya, Takeyuki Suzuki, Toshikazu Hirao,
Chem. Eur. J. 2016.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201604306