The rhodium(III)-catalyzed C–H activation of aromatic compounds allows the synthesis of complex heterocyclic molecules from simple starting materials in a single step. This method is particularly useful for the directed search for drug candidates and other biologically active molecules. However, controlling the chemo- and regioselectivity of the C–H-activation reactions is often challenging.
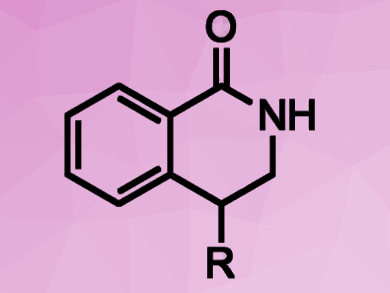
Dmitry Perekalin, Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, and colleagues have developed a rhodium(III)-based catalyst for C–H activation. The catalyst, [(C5H2tBu2CH2tBu)RhCl2]2, converts activated aromatic amides and alkenes into biologically active 4‐substituted dihydroisoquinolones (pictured). The desired products were obtained in yields of 72–97 %.
The cyclopentadienyl ligand of the catalyst complex was constructed via an unusual cyclization of three molecules of tert-butylacetylene. The bulky tert-butyl groups provide a high regioselectivity by blocking undesired reaction pathways. The designed catalyst could also help to improve regioselectivity of other C–H activation reactions.
- Rhodium(III) Complex with a Bulky Cyclopentadienyl Ligand as a Catalyst for Regioselective Synthesis of Dihydroisoquinolones through C–H Activation of Arylhydroxamic Acids,
Evgeniya A. Trifonova, Nikita M. Ankudinov, Maxim V. Kozlov, Mikhail Y. Sharipov, Yulia V. Nelyubina, Dmitry S. Perekalin,
Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 16570–16575.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201804050