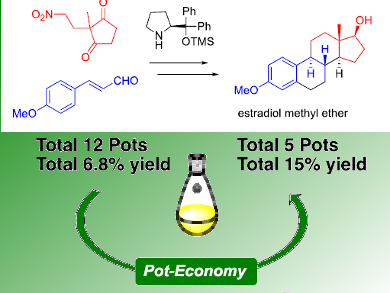
Estrogen is a member of the steroid family and is a female sex hormone. There are three estrogen compounds that have estrogenic hormonal activity in females; namely, estrone, estradiol, and estriol. Given their important biological activities, many total syntheses of these molecules have been developed.
Yujiro Hayashi and colleagues, Graduate School of Science Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, have accomplished an enantioselective total synthesis of estradiol methyl ether in a highly diastereo‐ and enantioselective manner. One of the key reactions is a domino reaction of diphenylprolinol silyl ether-mediated Michael reaction of nitroalkane and intramolecular aldol reaction to afford bicyclo[4.3.0]nonane derivatives with A, C, and D rings of the steroids as a single isomer with excellent enantioselectivity. Each reaction was optimized, and the total synthesis could be accomplished in 12 pots with 10 purifications using silica gel, resulting in an overall yield of 6.8 %.
After the completion of the synthesis, the team again optimized the reaction sequence and reaction conditions in terms of the pot economy. As a result, two reductions (LiBHEt3 and DIBAL) could be conducted in the same pot. Six reactions—namely, oxidation, hydrogenation, and formation of an acid chloride, Friedel–Crafts reaction, deprotection, and reduction—can be carried out in the last one-pot sequence. Thus, estradiol methyl ether can be synthesized using five reaction vessels with four purifications with a total yield of 15 %. In addition, the total time including the reaction, quenching, and purification was be reduced.
- Total synthesis of estradiol methyl ether and its five‐pot synthesis through the use of an organocatalyst,
Seitaro Koshino, Eunsang Kwon, Yujiro Hayashi,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201800910