Styrene is an important monomer for the production of polystyrene, its derivatives, and (block) co-polymers. The catalytic dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene is the major method for its synthesis. The process is carried out at temperatures above 600 °C with promoted iron catalysts in the presence of superheated steam. Due to its reversible and endothermic nature, a huge amount of energy is consumed.
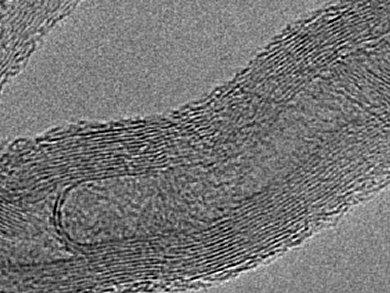
Bernd Ondruschka and colleagues, Friedrich-Schiller University Jena, Germany, developed purification and ozonation protocols for the functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) to modify their surface with respect to increasing the catalytic activity of the samples in the oxidative dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene (ODEB) to styrene. The modified MWCNT exhibit significantly improved conversion and styrene selectivity in the ODEB reaction. For instance, ozonation led to MWCNT-based catalysts revealing conversion and selectivity values of 80% and 92 %, respectively.
An increase in surface oxygen accompanied by high catalytic activity observed on the catalysts suggests that oxygen-containing groups are the dominant active sites for the reaction.
- Ozonated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as Highly Active and Selective Catalyst in the Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethyl Benzene to Styrene,
Nguyen V. Qui, Peter Scholz, Thomas F. Keller, Kilian Pollok, Bernd Ondruschka,
Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36 (2), 300–306.
DOI: 10.1002/ceat.201200354