Chalcogenoesters are important intermediates in synthetic organic chemistry. Among their uses, they have been employed as acylating reagents in the synthesis of acids, esters, amides, ketones, and aldehydes, as well as in the synthesis of natural compounds. The preparation of new frameworks with multiple ESiMe3 (E = S or Se) moieties would offer routes to the assembly of polythio- and selenoesters.
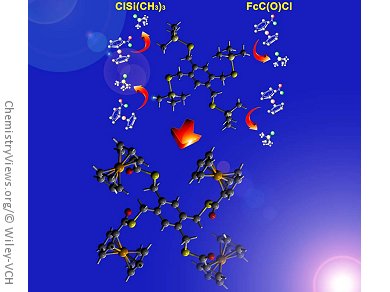
Along these lines, John F. Corrigan and his group, University of Western Ontario, London, Canada, have developed a straightforward synthesis of a novel series of di-, tri-, and tetra-polychalcogenotrimethylsilanes Ar(CH2ESiMe3)n (E = S or Se; n = 2–4). They are readily prepared in good yield by the reaction of lithium (trimethylsilyl) chalcogenolate Li[ESiMe3] with the corresponding di-, tri-, and tetra-bromobenzyl arene.
The team has demonstrated their use as “protected chalcogenides” for the facile preparation of polyferrocenylseleno- and thioester assemblies by reaction with ferrocene acid chloride. The synthetic methodology is likely to be useful in the synthesis of other chalcogenoesters. In addition, such polyredox chacogenides are unique and may serve as a basis for the construction of original nanomaterials.
- New Polydentate Trimethylsilyl Chalcogenide Reagents for the Assembly of Polyferrocenyl Architectures,
M. A. Fard, B. Khalili Najafabadi, M. Hesari, M. S. Workentin, J. F. Corrigan,
Chem. Eur. J. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201400185