Insulin is a life-saving drug for people suffering from diabetes. Unfortunately, insulin has to be taken in the form of subcutaneous injections because its oral administration is impossible. This is due to the fact that insulin is reduced to fragments in the digestive tract and withheld by the gastrointestinal (GI) tract barriers, which include a mucus layer and the intestinal epithelium.
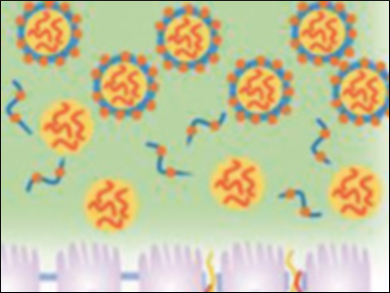
Hai‐Quan Mao, Sun Yat‐sen University, Guangzhou, China, and Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA, Zhijia Liu and Yongming Chen, Sun Yat‐sen University, and colleagues have used core-shell nanoparticles to enhance the oral delivery efficiency of insulin. First, positively charged nanoparticles were synthesized by an electrostatic complexation between the insulin (pictured red) and N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-3-trimethylammonium-chloride-modified chitosan (HTCC, pictured yellow). Then, the surface of these particles was coated with thiolated hyaluronic acid (pictured blue/orange).
The thiolated nanoparticles show improved intestinal retention, greater mucus penetration ability, and enhanced transepithelial transport efficiency. Hyaluronic acid facilitates the particles’ penetration through the mucus layer and thiolated compounds improve the intestinal retention and mucosal transport by forming disulfide bonds with components of the mucus. Tests with Type 1 diabetic rats show that the bioavailability of insulin in the nanoparticles reached 11.3 % after oral administration. According to the researchers, these results demonstrate that the developed core–shell nanoparticles are a promising oral delivery vehicle for protein drugs such as insulin.
- Uniform Core-Shell Nanoparticles with Thiolated Hyaluronic Acid Coating to Enhance Oral Delivery of Insulin,
Houkuan Tian, Zhiyu He, Chengxin Sun, Chengbiao Yang, Pengfei Zhao, Lixin Liu, Kam W. Leong, Hai-Quan Mao, Zhijia Liu, Yongming Chen,
Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201800285
Also of Interest
- Insulin Tablets Instead of a Syringe?,
Marek Czykanski,
Chemistryviews.org 2018.
Ionic liquids for oral insulin delivery