Nitrofurfural is a highly important chemical for the production of nitrofuran-based Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) with antibacterial properties. It is synthesized by the nitration of furfural, a compound derived from biomass waste. However, furfural has a delicate heteroaromatic structure and cannot withstand harsh nitration conditions, often resulting in low yields and poor reproducibility. Although milder nitrating agents, like acetyl nitrate, are more suitable, their conventional preparation methods concern significant safety risks due to the explosive nature of acetyl nitrate. Additionally, the standard in situ generation of acetyl nitrate still exposes furfural to harsh reaction conditions.
Monbaliu and co-workers addressed this issue in their recent research article.1 Their work represents a major advancement in the synthesis of nitrofuran-based pharmaceuticals by developing a safe, efficient, and highly automated continuous flow platform for the nitration of furfural. This flow synthesis set-up generates acetyl nitrate in situ under mild conditions which avoids the need to handle or store the explosive chemical directly. It also integrates filtration and separation units, along with sensors and Process Analytical Technology (PAT) tools, to ensure smooth operation, safety, and reproducibility. This flow synthesis is highly efficient and can be operated by a single person.
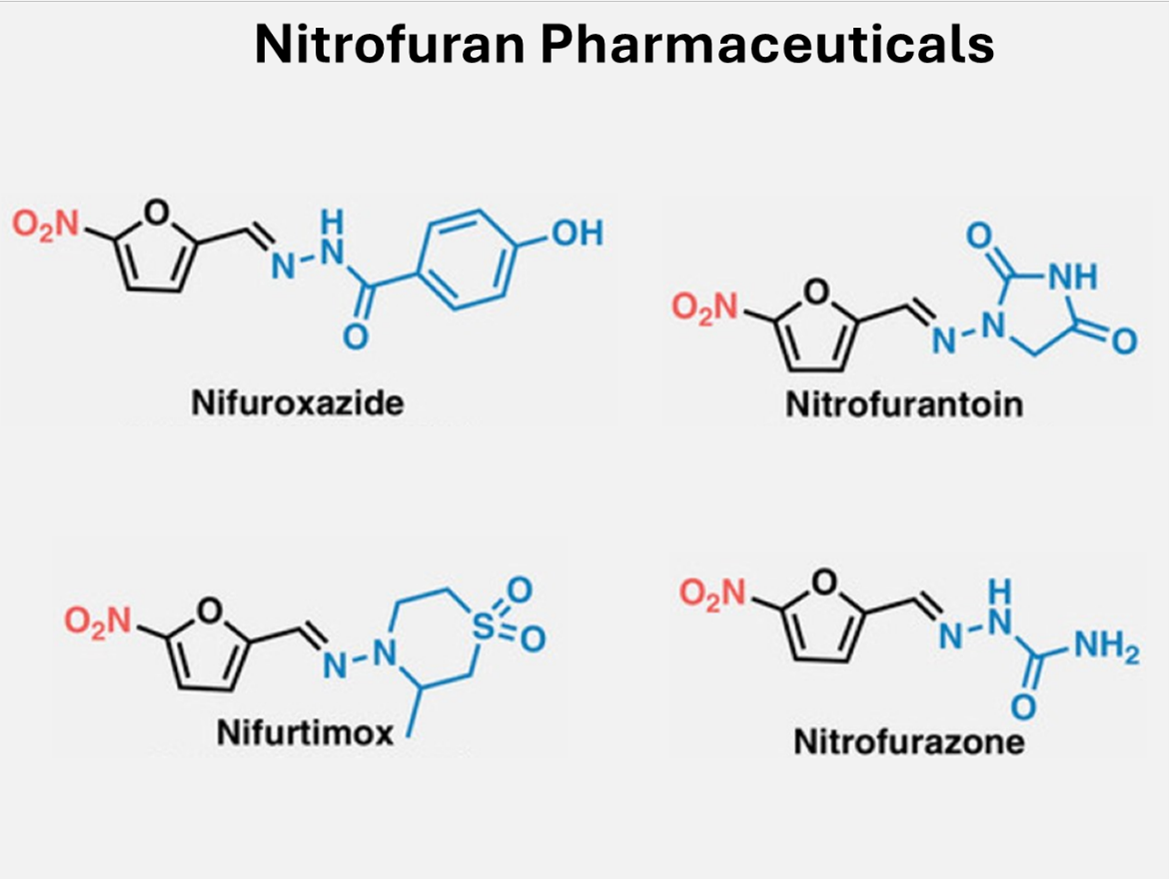
After the successful nitration of furfural, this set-up was used to synthesize four nitrofuran APIs (nifuroxazide, nifurtimox, nitrofurantoin, and nitrofurazone). It produces nitrofurantoin, one of the best-selling nitrofuran APIs, in less than five minutes, with a 94% isolated yield.
This innovation offers a significant improvement for pharmaceutical manufacturing, combining safety, speed, and reproducibility in the production of valuable antimicrobial compounds.
- Continuous Flow Synthesis of Nitrofuran Pharmaceuticals Using Acetyl Nitrate
Hubert Hellwig, Loïc Bovy, Kristof Van Hecke, Cornelis P. Vlaar, Rodolfo J. Romañach, Md. Noor-E-Alam, Allan S. Myerson, Torsten Stelzer, and Jean-Christophe M. Monbaliu
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025
doi.org/10.1002/anie.202501660