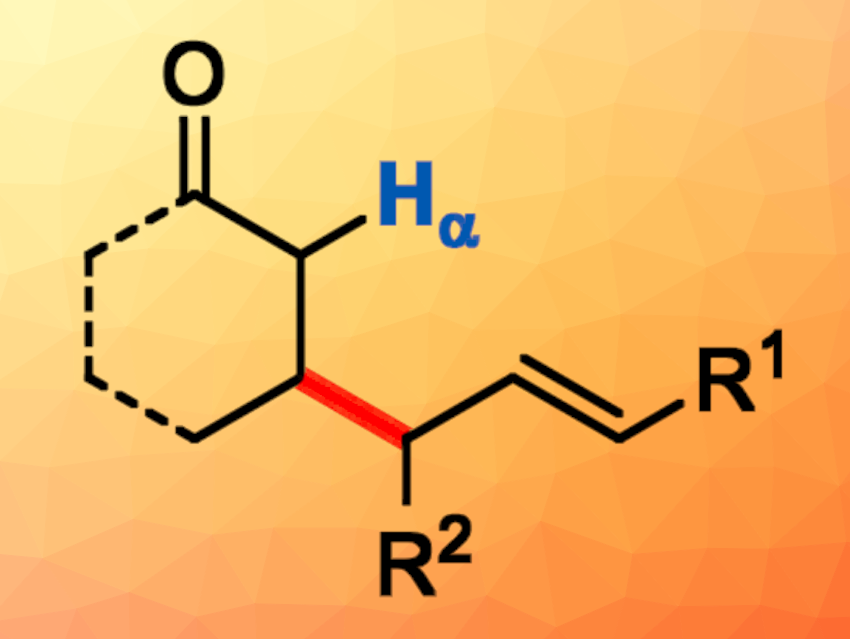
Tsuji-Trost reactions between carbonyl compounds and allylic precursors are useful tools in organic synthesis. The α-C–H bond of carbonyl compounds is far more acidic than the β-C–H bond, so they undergo highly regioselective allylation at the α-position. Obtaining the corresponding β-allylation products can be challenging.
Armido Studer, University of Münster, Germany, and colleagues have developed a formal intermolecular β-C–C bond formation reaction between a broad range of aldehydes or ketones and different allyl electrophiles, using cooperative nickel and photoredox catalysis (general reaction pictured below). In this approach, the aldehydes or ketones are first transformed into the corresponding silyl enol ethers. Single electron oxidation using a photocatalyst and deprotonation then lead to an allylic β-C-radical. Finally, a Ni-catalyzed Tsuji-Trost allylation step gives the desired product.
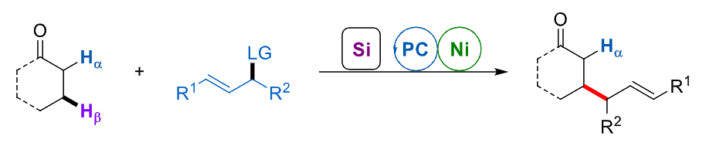
The team used NiCl2·glyme (glyme = dimethyl glycol) as the precatalyst together with diimine ligands and 4-CzIPN (1,2,3,5-tetrakis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,6-dicyanobenzene) as the photoredox catalyst. The reactions were performed in MeCN under blue light irradiation. The researchers obtained the desired allylation products in moderate to good yields. The approach features mild conditions, excellent regioselectivity, and wide functional group tolerance.
- Regioselective Formal β‐Allylation of Carbonyl Compounds Enabled by Cooperative Nickel and Photoredox Catalysis,
Kun Liu, Zhe Wang, Augustinus N. Künzel, Marcus Layh, Armido Studer,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202303473