The synthesis of CH4 from CO2 and H2 can be used to store energy and, e.g., compensate for the fluctuating production of renewable energy. Supported nickel nanoparticles are a cost-efficient catalyst for this reaction. However, they tend to aggregate at high temperatures, which deactivates the catalyst.
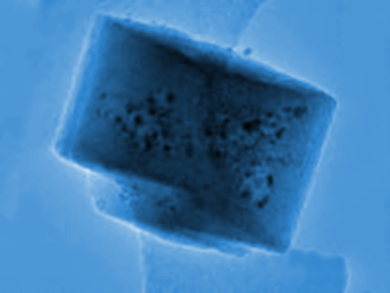
Jerrik Mielby, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, and colleagues have developed a method to encapsulate Ni nanoparticles in a zeolite, namely a modified silicalite-1, to prevent this problem. The team used an aqueous solution of ammonium hydroxide and cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to selectively desilicate the zeolite and create mesopores. The material was then calcined, dried, and combined with a solution if Ni(NO3)2 to produce the encapsulated Ni nanoparticles (pictured).
The synthesized catalyst has a high catalytic activity for CO2 methanation with about 60 % conversion at 450 °C. After 50 hours of operation, no change in activity or selectivity of the reaction was observed. The researchers attribute the activity to the small size and good dispersion of the Ni nanoparticles in the modified zeolite.
- Methanation of CO2 over Zeolite-Encapsulated Nickel Nanoparticles,
Farnoosh Goodarzi, Liqun Kang, Feng Ryan Wang, Finn Joensen, Søren Kegnaes, Jerrik Mielby,
ChemCatChem 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201701946