Combinatorial Chemistry
Combinatorial libraries are a key component of the chemist’s toolkit for ligand screening. Dynamic combinatorial libraries add a new dimension by interlinking synthesis and screening. Sarah H. Hewitt and Andrew J. Wilson, University of Leeds, UK, have developed a dynamic combinatorial library for the screening of supramolecular ligand structures that recognize protein surfaces and could interfere with protein–protein interaction.
Combinatorial chemistry has been embraced by the pharmaceutical industry because it allows chemists to create large amounts of molecules and test them for desired properties, for example, binding affinities to a therapeutically important target. Synthesis and screening are linked in dynamic combinatorial chemistry as the dynamic combinatorial libraries can shift their product distribution in response to target binding. This product-amplification process generates supramolecular structures that are otherwise difficult to access and allows the fast identification of binding architectures, for example, inhibitors binding to the active site of an enzyme.
However, protein surfaces are large three-dimensional structures with patches of different hydrophobicity, acidity, and basicity, found in disparate positions on their surface. Therefore, the screening of inhibitors of protein–protein interactions must involve more complex ligands than those needed for active site recognition. “We needed to identify reversible chemistry and analytical methodology which would be compatible with the idea of doing dynamic combinatorial chemistry for protein surface recognition,” says Wilson.
Hydrazone-Functionalized Surface Mimetics
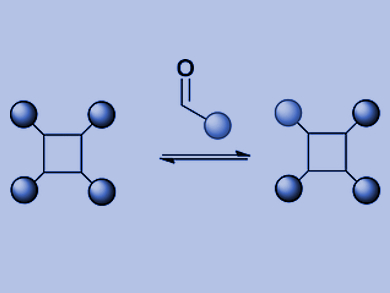
The scientists chose a tetraphenylporphyrin scaffold bearing four hydrazides and substituted benzaldehydes as recognition arms that would reversibly link with the hydrazides to form hydrazones. The porphyrins are established scaffolds for protein surface recognition, but the hydrazone chemistry is synthetically challenging. “We’ve got a scaffold with four hydrazones so we can do exchange chemistry on four different positions,” says Wilson. In addition, reversible hydrazone-forming chemistry usually takes place at an acidic pH, but proteins prefer a neutral pH. The scientists addressed this problem by adding an aniline-based catalyst, which pushed the hydrazone exchange reaction towards thermodynamic equilibrium at close to neutral pH.
In the first setup of this model library, the researchers tried two substituted aldehyde ligands, which formed an equilibrium with the benzaldehyde-derived hydrazone. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that the product distribution was at thermodynamic equilibrium, and the ligands indeed exchanged by a reversible reaction. This means that the conditions for a dynamic combinatorial library for protein surface recognition were set. Next, the scientists plan to elaborate this approach to study the protein-directed selection of protein surface mimetics.
- Generation of Dynamic Combinatorial Libraries Using Hydrazone-Functionalized Surface Mimetics,
Sarah H. Hewitt, Andrew J. Wilson,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1872–1879.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201800022