Drugs for metabolic disorders and aging-related diseases are highly important in an aging society. Designing efficient therapeutics by targeting drugs to specific cells has attracted intense attention. Organelle-targeted drug-delivery is a strategy to improve the therapeutic efficacy of drugs even more by directly delivering them to the site of action within target cells and minimizing side effects and required dosages.
Peroxisomes (a type of organelle found in almost all eukaryotic cells) have, so far, been underestimated as an important target among the subcellular organelles. However, they have important metabolic functions—including hydrogen peroxide metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and lipid synthesis—and are relevant to severe human genetic disorders.
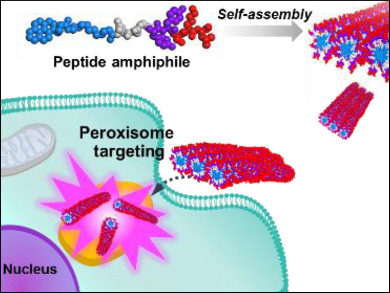
Eun Hee Han, Korea Basic Science Institute, Cheongju, Republic of Korea, Eunji Lee, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Republic of Korea, and colleagues have developed a peroxisome-targeting supramolecular nanoprobe. It is based on the self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles in water. A fluorescent probe (pyrene, pictured blue) was decorated with the short tripeptide SKL-COOH (pictured red, S: serine, K: lysine, and L: leucine). The peptide targets the peroxisome (pictured yellow) and is recognized by a receptor in the peroxisome membrane. The distribution of the nanostructures within human cancer cells was measured using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and three-dimensional transmission electron microscopy tomography (3D-TEMT).
According to the researchers, this is the first report on a supramolecular synthetic nanoprobe that has been used for peroxisome-targeting in mammalian cells. The result could significantly contribute to the development of organelle-targeted next-generation nanomedicine.
- Peroxisome-targeted supramolecular nanoprobes assembled with pyrene-labelled peptide amphiphiles,
Eunji Lee, Inhye Kim, Woo-Young Bang, Sooyong Kim, Seon-Mi Jin, Ju-Yong Hyun, Eun Hee Han,
Chem. Asian J. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201800863