The oxepine ring and its hydrogenated versions are present in a wide variety of natural products. The total synthesis of these products has mainly been achieved using C–C-bond-forming ring-closing metathesis or C–O-bond-forming nucleophilic substitutions. Sigmatropic rearrangements of 2-vinylcyclopropanecarbonyl substrates could be an alternative to these reactions. However, this approach has been hampered by the metastability of the 2,5-dihydrooxepine intermediates, which strongly depends on their substitution pattern.
Wei Zhang, Bastien Nay, Gilles Frison (Ecole Polytechnique de Paris, France), and colleagues have developed a one-pot method to synthesize bicyclic 2,5-dihydrooxepines. The team used a tandem vinylcyclopropanation/retro-Claisen rearrangement (pictured below), starting from 1,3-cyclohexadione derivatives. These reactions were carried out under strict temperature control to minimize the formation of competing dihydrofuran products.
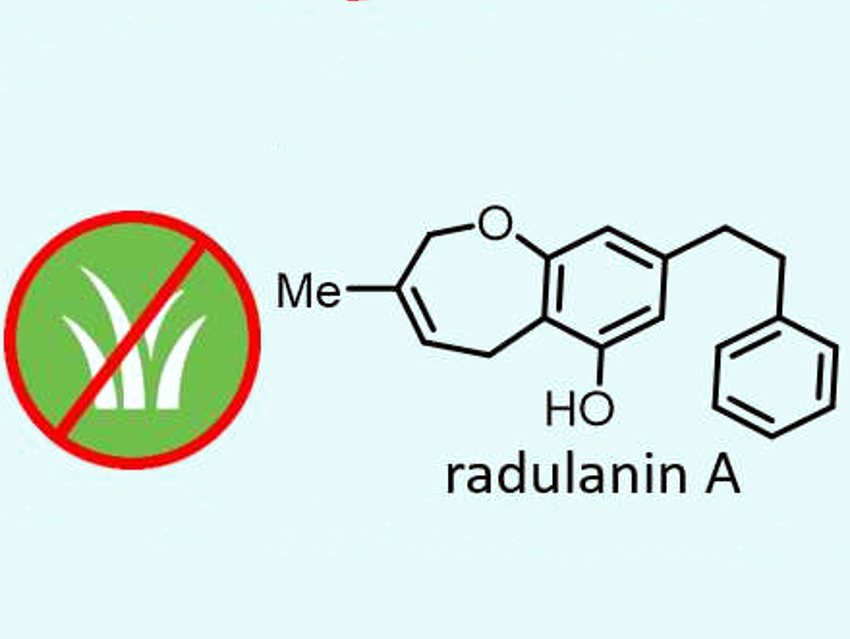
The one-pot approach was successfully used for a short total synthesis of radulanin A (pictured above), a natural 2,5-dihydrobenzoxepine isolated from liverwort. The team used thale cress seedlings to evaluate the herbicidal potential of this natural product. Its activity was comparable to that of glyphosate, which is used as a reference herbicide. This discovery has been patented and the team hopes that it leads to a new class of natural weed-killing compounds.
.jpg)
- One-Pot Synthesis of Metastable 2,5-Dihydrooxepines through Retro-Claisen Rearrangements: Method and Applications,
Wei Zhang, Emmanuel Baudouin, Marie Cordier, Gilles Frison, Bastien Nay,
Chem. Eur. J. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201901675