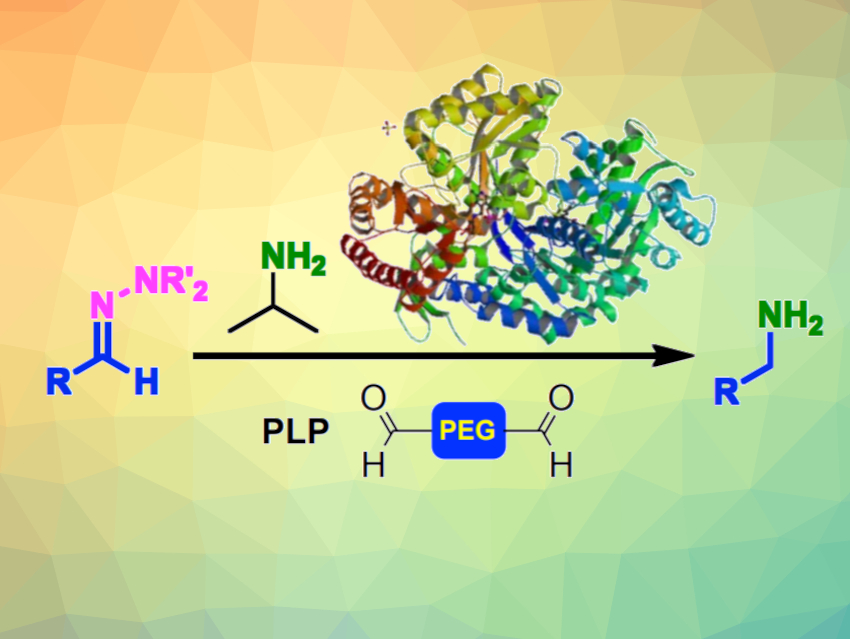
Biocatalysis, i.e., using enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions, has become increasingly useful. The benefits of enzymes are that they are sustainable, non-toxic, and biodegradable. Transaminase enzymes, for example, have been widely used for the amination of aldehydes and ketones.
Helen C. Hailes, University College London, UK, and colleagues have used transaminases to convert a range of hydrazones into amine products. The reactions were performed in aqueous media using an amine donor and the cofactor pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP). The corresponding amines were readily formed. Yields increased when an additional electrophile was added to “trap” the hydrazine released in the reaction. For this, the team used polyethylene glycol (PEG)-based aldehydes.
The team demonstrated the utility of the reaction by using it on a (S)-(–)-1-amino-2-(methoxymethyl)pyrrolidine (SAMP)-based hydrazone. SAMP can be used as a chiral auxiliary for the asymmetric α-alkylation of aldehydes and ketones. It was found that a transaminase can remove the SAMP auxiliary in one step, providing a high-yielding and sustainable method to form β-substituted chiral amines.
- Direct Conversion of Hydrazones to Amines using Transaminases,
Helen Claire Hailes, Eve Carter, Fabiana Subrizi, John Ward, Tom Sheppard,
ChemCatChem 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202101008