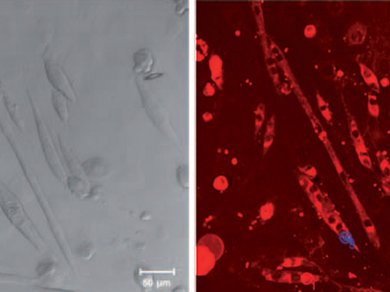
The ability of a compound to treat diabetes is marked by an increase in the rate of glucose uptake in cells. This rate can be monitored by using radioisotope (14C or 3H)-labeled 2-deoxyglucose analogues—the current gold standard for determining cellular glucose uptake.
Seung Bum Park and colleagues, Seoul National University, Korea, have developed a novel bioprobe, GB2-Cy3, for real-time monitoring of glucose uptake. They synthesized a series of fluorescent glucose analogues by adding the water-soluble, cyanine-based dye, Cy3, to the α-anomeric position of ᴅ-glucose with various linkers.
GB2-Cy3 was shown to be ten times more sensitive than 2-NBDG, a leading fluorescent glucose bioprobe, and could be utilized in three different systems to monitor glucose in metabolically active C2C12 myocytes.
The real-time monitoring of glucose uptake in living cells could have significant impact for diagnosing metabolic diseases.
- Development of Fluorescent Glucose Bioprobes and Their Application on Real-Time and Quantitative Monitoring of Glucose Uptake in Living Cells
H. Y. Lee, J. J. Lee, J. Park, S. B. Park,
Chem. Eur. J. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201002560