The annual CWTS Leiden University Ranking for 2018 has been published by the Centre for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden University, The Netherlands. The Leiden Ranking is based on bibliographic data from the Web of Science database by Clarivate Analytics. It provides both a size-dependent rating, which is based on the absolute number of top-cited publications, and a size-independent list, where the performance of a university is measured relative to its publication output. The 2018 ranking includes 938 universities from 55 different countries.
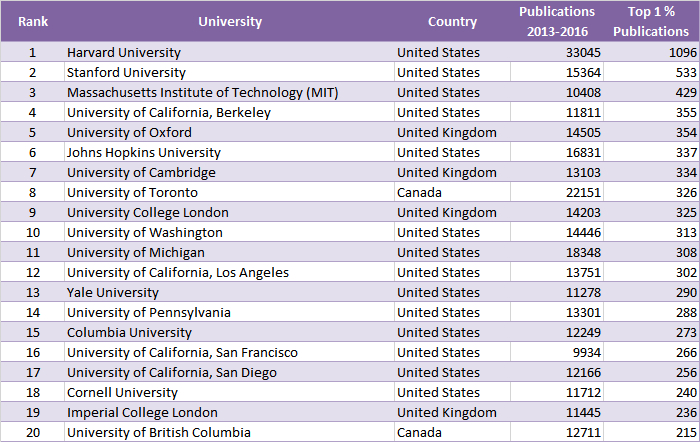
This year, the top 20 is made up of US, UK, and Canadian institutions. The three highest-ranked universities overall (based on top 1 % most cited papers) are Harvard University, Stanford University, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), all USA. The top institution in a non-English-speaking country is Tsinghua University, China, at rank 22, followed by the highest ranked European institution, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich.
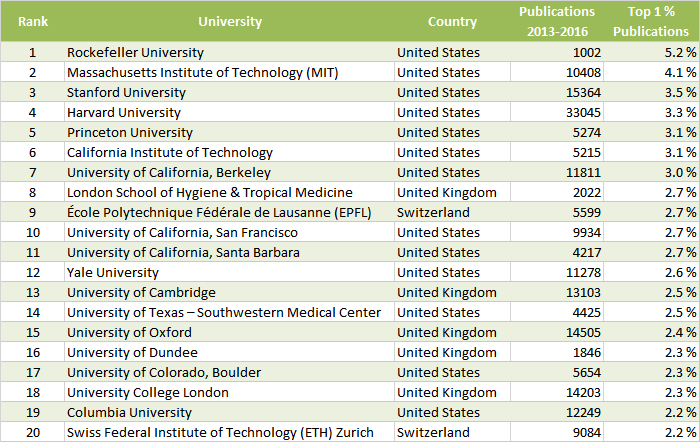
Considering size-independent values, Rockefeller University, New York, USA, is ranked at number 1, followed by MIT and Stanford University. The highest-ranked European institution in this category is the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL) Lausanne at rank 9, the top Asian institution is the Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, China, at rank 43.
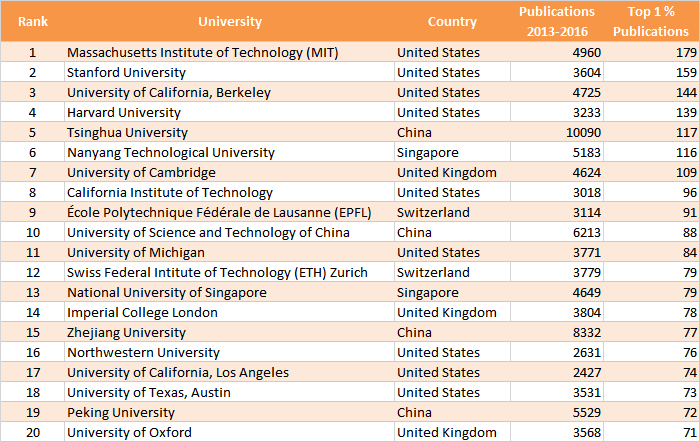
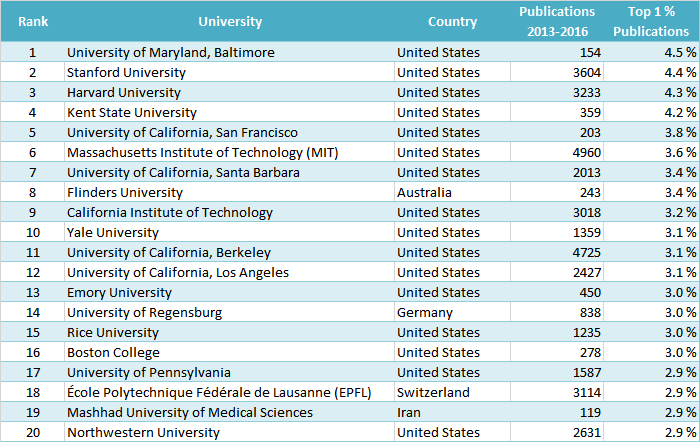
In the physical sciences, which include chemistry and related disciplines, the top rank in the size-dependent rating is occupied by MIT. In the size-independent ranking, the University of Maryland, Baltimore, USA, is ranked at number one in these fields.
Size-Dependent Ranking (All Sciences)
(by the number of the university’s publications belonging to the top 1 % most frequently cited)
Size-Independent Ranking (All Sciences)
(by proportion of the university’s publications belonging to the top 1 % most frequently cited)
Size-Dependent Ranking (Physical Sciences and Engineering)
(by the number of the university’s publications belonging to the top 1 % most frequently cited)
Size-Independent Ranking (Physical Sciences and Engineering)
(by proportion of the university’s publications belonging to the top 1 % most frequently cited)
Methodology
The Leiden Ranking is based exclusively on bibliographic data covering the years 2013–2016 from the Web of Science database produced by Clarivate Analytics. Book publications, publications in conference proceedings, publications in journals not indexed in Web of Science, and publications in other languages than English are not included.
The ranking offers the following indicators of the scientific impact of a university:
- P(top 1 %) and PP(top 1 %)
The number and the proportion of a university’s publications that, compared with other publications in the same field and in the same year, belong to the top 1% most frequently cited. - P(top 5 %) and PP(top 5 %)
The number and the proportion of a university’s publications that, compared with other publications in the same field and in the same year, belong to the top 5% most frequently cited. - P(top 10 %) and PP(top 10 %)
The number and the proportion of a university’s publications that, compared with other publications in the same field and in the same year, belong to the top 10% most frequently cited. - P(top 50 %) and PP(top 50 %)
The number and the proportion of a university’s publications that, compared with other publications in the same field and in the same year, belong to the top 50% most frequently cited. - TCS and MCS
The total and the average number of citations of the publications of a university. - TNCS and MNCS
The total and the average number of citations of the publications of a university, normalized for field and publication year. An MNCS value of two, for instance, means that the publications of a university have been cited twice above the average of their field and publication year.
The ranking provides statistics for the following five fields of science:
- Biomedical and health sciences
- Life and earth sciences
- Mathematics and computer science
- Physical sciences and engineering
- Social sciences and humanities
- CWTS Leiden Ranking 2018,
Centre for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden University, The Netherlands
Also of Interest
- World University Rankings 2018,
ChemistryViews.org 2017.
University of Oxford keeps top spot in Times Higher Education university ranking - Academic Ranking of World Universities 2017,
ChemistryViews.org 2017.
Harvard University keeps top rank for the 15th consecutive year


