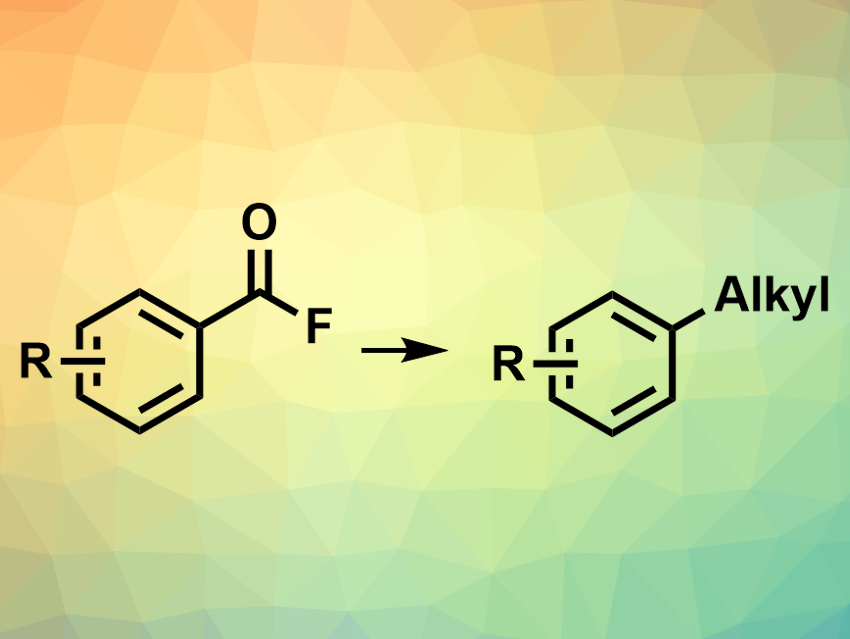
Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions are widely used in organic synthesis. However, the construction of C(sp2)–C(sp3) bonds is more challenging than, for example, that of C(sp2)–C(sp2) bonds due to side reactions. New methods for aryl–alkyl couplings are, thus, useful.
Yasushi Nishihara, Okayama University, Japan, and colleagues have developed an approach for the decarbonylative alkylation of acyl fluorides (pictured), using a palladium complex as the catalyst and alkylboranes as reactants. The team used Pd(acac)2 as a catalyst (acac = acetylacetonate), bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (DPPE) as a ligand, and potassium fluoride as an additive. The reaction was performed at 140 °C in a toluene/dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) mixture. A variety of aromatic acyl fluorides was reacted with a range of B-alkyl-9-BBN reagents (9-BBN = 9-borabicyclo(3.3.1)nonane) to give the desired alkylated products in moderate to excellent yields.
The reaction provides good functional group tolerance. According to the researchers, the hemilabile bisphosphine ligand plays an important role in avoiding side reactions, such as β-hydride elimination, that can hamper C(sp2)–C(sp3) couplings.
- Palladium-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Alkylation of Acyl Fluorides,
Liyan Fu, Qiang Chen, Zhenhua Wang, Yasushi Nishihara,
Org. Lett. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00542