Heteroaromatics are often found in pharmaceutically active compounds. Their functionalization often starts from readily available halogenated derivatives. For example, one common reaction is the nucleophilic aromatic substitution at electron-poor heteroaromatics using a sulfur nucleophile. However, there had been no equivalent reaction with a wide substrate scope for the thiolation of electron-rich heteroarenes so far.
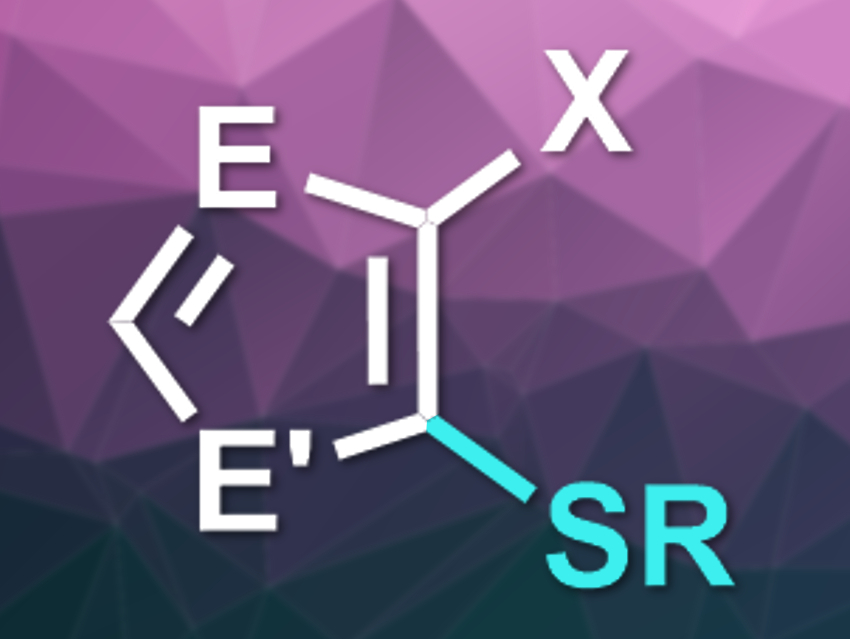
Frank Glorius, University of Münster, Germany, and colleagues have developed a photocatalyzed radical reaction for the selective thiolation of halogenated, electron-rich heteroaromatics (product pictured, E = N, CR; E’ = NR,S,O; X = Br, Cl). The team used [Ir(dF(CF3)ppy)2dtbbpy)][PF6] (dF(CF3)ppy = 3,5-difluoro-2-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]phenyl, dtbbpy = di-tert-butylbipyridine) as the photocatalyst, N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA) as the solvent, and blue LEDs as the light source. The reaction between a wide variety of (multi)halogenated imidazoles, thiophenes, furans, or pyrroles and primary, secondary, or benzylic thiols then proceeded at room temperature.
The desired thiolated products were obtained in moderate to excellent yields, depending on the reaction partners. The reaction is site-selective and targets the most electron-rich position of the substrate. The conditions are mild and the protocol can be used for the functionalization of complex molecules.
- Site-Selective Thiolation of (Multi)halogenated Heteroarenes,
Frederik Sandfort, Tobias Knecht, Tobias Pinkert, Constantin G. Daniliuc, Frank Glorius,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c01630