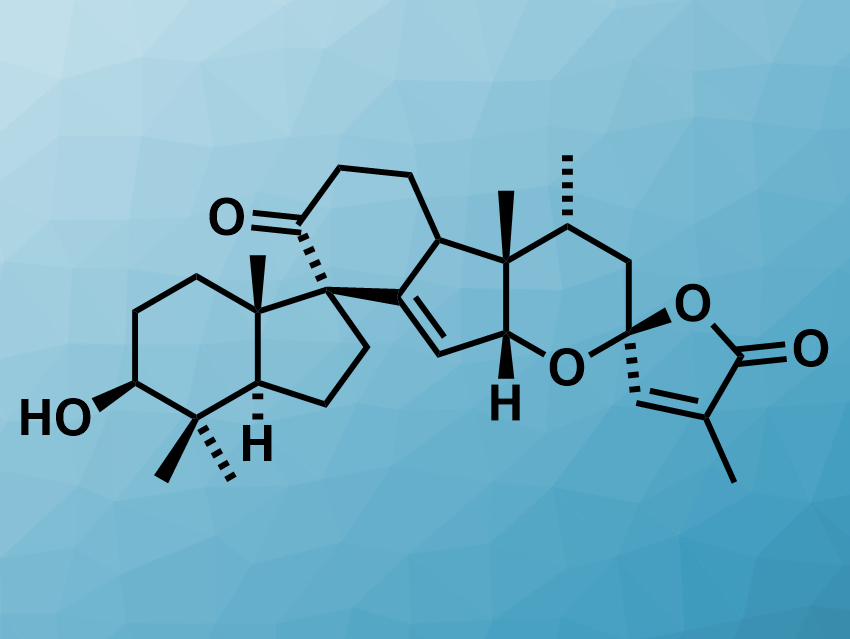
Spirochensilide A (pictured) is a natural product with two spirocyclic units. It has been isolated from Abies chensiensis, or Shensi fir, a plant native to parts of China and India. Extracts from these plants are bioactive, e.g., with antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory effects. Spirochensilide A, in particular, affects the production of NO and could be useful for studies of inflammatory diseases. NO is a signaling molecule that plays a key role in the pathogenesis of inflammation.
Xin-Ting Liang, Jia-Hua Chen, Peking University, Beijing, China, Zhen Yang, Peking University and Shenzhen Wan Laboratory, China, have performed the first asymmetric total synthesis of (−)-spirochensilide A. The team first prepared a bicyclic intermediate via a Lewis-acid induced cyclization and a semipinacol rearrangement. A Sonogashira reaction was used to install an alkyne-bearing sidechain on this intermediate. A tungsten-mediated cyclopropene-based Pauson–Khand reaction was then used to form a cyclopentenone. Finally, the spiroketal unit was created stereoselectively using a furan-based oxidative cyclization.
Overall, the synthesis involved 22 steps and gave a total yield up to 2.2 %. According to the researchers, they obtained over 150 mg of product in their first round of synthesis. The NMR spectroscopy and optical rotation data are in agreement with those reported for (−)-Spirochensilide A.
- Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (−)-Spirochensilide A,
Xin-Ting Liang, Jia-Hua Chen, Zhen Yang,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c02522