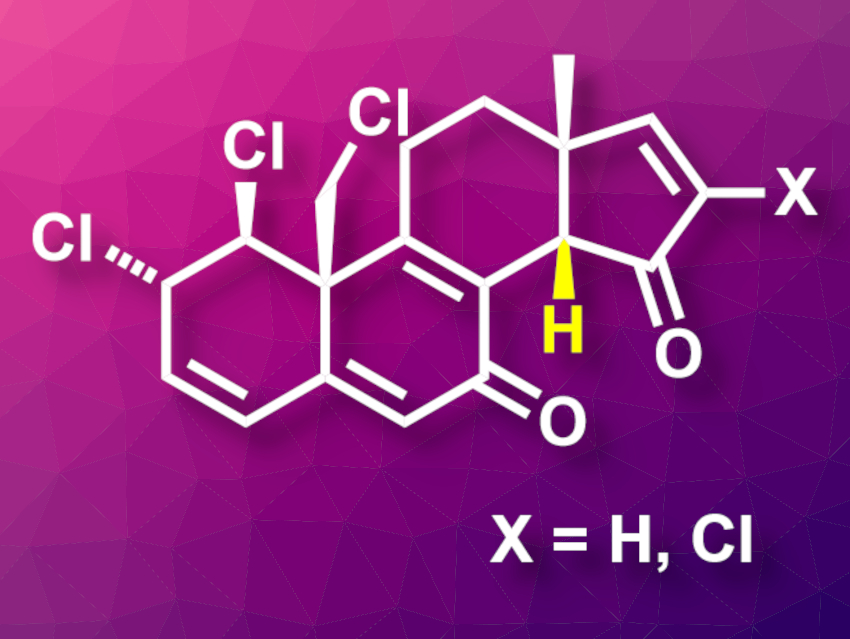
Clionastatins A and B (pictured, X = H for clionastatin A, X = Cl for clionastatin B) are polychlorinated steroids that were first isolated from the sponge Cliona nigricans. Their proposed structure has been based on NMR spectroscopic data, and no X-ray crystallographic structures have been available. The compounds have shown cytotoxicity against tumor cells.
Jinghan Gui, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and colleagues have performed the first total synthesis of polychlorinated steroids clionastatins A and B and revised the proposed stereochemistry of the compounds. The team used a fragment-based approach, in which a radical coupling between an acyl telluride and an enone is used to combine the fragments. Key steps in the synthesis of the acyl telluride fragment are a Corey–Bakshi–Shibata reduction and an Ireland–Claisen rearrangement. After the fragment coupling, an intramolecular Heck reaction was used to close the ring system. The resulting intermediate was chlorinated and desaturated to give clionastatin A. Clionastatin B was obtained from clionastatin A via a regioselective chlorination with Et4NCl3.
Clionastatins A and B were obtained in 16 and 17 steps, respectively. The team found that the optical rotations and 1H NMR spectra of the synthesized compounds were in good agreement with the isolated natural products. This led them to revise the previously proposed structure of clionastatins A and B, in which the configuration at C14 (pictured in yellow) had been inverted. In the revised structure, the C/D-ring system is cis-fused.
- Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Clionastatins A and B,
Wei Ju, Xudong Wang, Hailong Tian, Jinghan Gui,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c07511