Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a pathogenic microorganism that infects the lungs and causes a severe pulmonary disease known as tuberculosis. Multidrug resistant mycobacterial strains are spread worldwide and they constitute a major health issue in many countries.
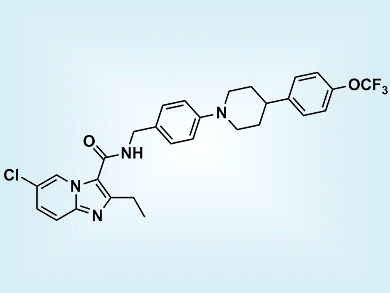
Kevin Pethe, Pasteur Institute Korea, Korea, and colleagues discovered Q203 (pictured), an imidazopyridine amide derivative that kills drug-resistant tuberculosis strains through a novel mechanism. Unlike other anti-tubercular agents, the new compound targets the respiratory cytochrome bc1 complex, a coenzyme that provides mycobacteria with the energy necessary to proliferate.
When tested in infected mice, Q203 successfully treated tuberculosis without causing noticeable side effects. No signs of toxicity were observed even when Q203 was administered at high doses for a prolonged period of time. Q203 is, thus, a promising new drug for the treatment of tuberculosis.
- Discovery of Q203, a potent clinical candidate for the treatment of tuberculosis,
Kevin Pethe, Pablo Bifani, Jichan Jang, Sunhee Kang, Seijin Park, Sujin Ahn, Jan Jiricek, Juyoung Jung, Hee Kyoung Jeon, Jonathan Cechetto, Thierry Christophe, Honggun Lee, Marie Kempf, Mary Jackson, Anne J Lenaerts, Ha Pham, Victoria Jones, Min Jung Seo, Young Mi Kim, Mooyoung Seo, Jeong Jea Seo, Dongsik Park, Yoonae Ko, Inhee Choi, Ryangyeo Kim, Se Yeon Kim, SeungBin Lim, Seung-Ae Yim, Jiyoun Nam, Hwankyu Kang, Haejin Kwon, Chun-Taek Oh, Yoojin Cho, Yunhee Jang, Junghwan Kim, Adeline Chua, Bee Huat Tan, Mahesh B Nanjundappa, Srinivasa P S Rao, Whitney S Barnes, René Wintjens, John R Walker, Sylvie Alonso, Saeyeon Lee, Jungjun Kim, Soohyun Oh, Taegwon Oh, Ulf Nehrbass, Sung-Jun Han, Zaesung No, Jinhwa Lee, Priscille Brodin, Sang-Nae Cho, Kiyean Nam, Jaeseung Kim,
Nat. Med. 2013.
DOI: 10.1038/nm.3262