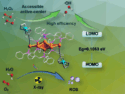
Prof. Geoffrey Bothun, Prof. Arijit Bose and Yanjing Chen, University of Rhode Island, developed a new system for the controlled delivery of pharmaceutical drugs. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embed in the shell of a liposome release a model drug by making the shell leaky when heat-activated in an alternating current electromagnetic field operating at radio frequencies.
The rate and extent of the release of a model drug molecule is controlled by varying the nanoparticle loading and the magnetic field strength.
The liposomes self-assemble because portions of the lipids are hydrophilic and others are hydrophobic. When lipids and nanoparticles are mixed in a solvent, water is added and the solvent evaporated, the materials automatically assemble themselves into liposomes.
The concept of loading nanoparticles within a hydrophobic shell to focus the activation is brand new. It works because the leakiness of the shell is ultimately what controls the release of the drugs.