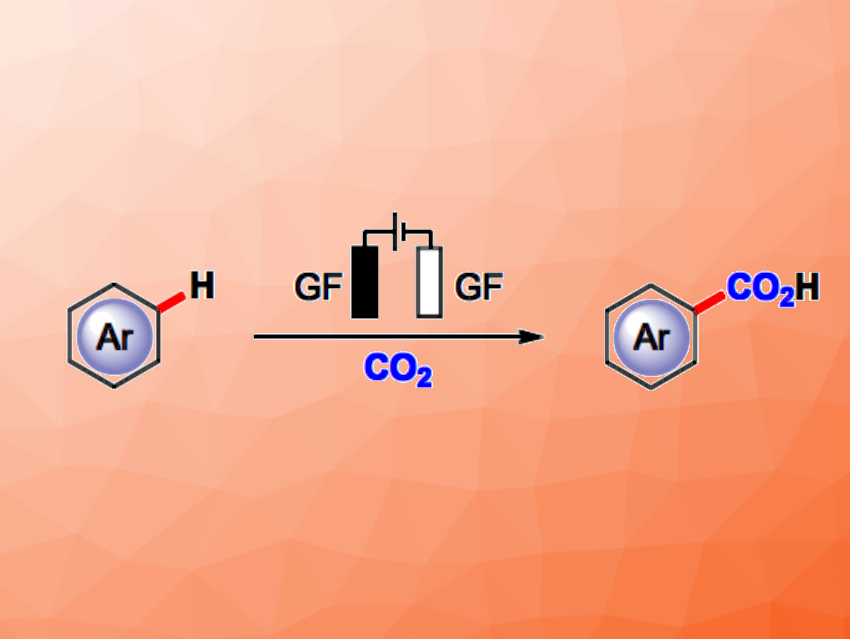
Aromatic carboxylic acids play important roles, e.g., in organic and pharmaceutical chemistry. Thus, methods for their “green” preparation from readily available starting materials with high selectivity, high efficiency, and low costs are attractive research targets. One possible approach would be the direct C−H carboxylation of arenes with CO2, which has a high atom economy, uses easily obtained starting materials, and converts the greenhouse gas CO2 into useful products.
Youai Qiu, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, and colleagues have developed a site-selective electrochemical C−H carboxylation of arenes with CO2 (pictured). The team reacted a variety of arenes, heteroarenes, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with CO2 (1 atm) in an undivided electrochemical cell with graphite felt (GF) electrodes, using Et4NI as the electrolyte and dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent.
The desired products were obtained in moderate to good yields. The reaction has a broad substrate scope, excellent atom economy, and high selectivity. In addition, the method is catalyst-free and base-free. The team proposes a mechanism that involves the direct reduction of the arene at the cathode to form the corresponding radical anion, followed by the reaction with CO2 and a protonation step. For substrates with a reduction potential that is more negative than that of CO2, the arenes could react with a CO2 radical anion generated by electroreduction.
- Site‐Selective Electrochemical C−H Carboxylation of Arenes with CO2,
Zhiwei Zhao, Yin Liu, Siyi Wang, Shunyao Tang, Dengke Ma, Zile Zhu, Chengcheng Guo, Youai Qiu,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202214710