Scintillators are materials that show luminescence when excited by high-energy radiation. They can absorb and down-convert high-energy radiation, such as X-rays or γ-rays, into ultraviolet/visible/infrared light. This can be useful, for example, in radiation leak monitoring, medical imaging, and security applications.
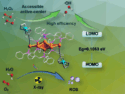
Xiao-Wu Lei, Jining University, Qufu, China, Yuan-Chun He, Qufu Normal University, China, and colleagues have discovered zero-dimensional three hybrid manganese halides that can act as highly efficient, lead-free scintillators. The team prepared single crystals of three compounds of the type A2MnBr4 (A = BzTPP, Br-BzTPP, and F-BzTPP, BzTPP = benzyltriphenylphosphonium) from MnBr2·4H2O and the corresponding BzTPP derivatives.
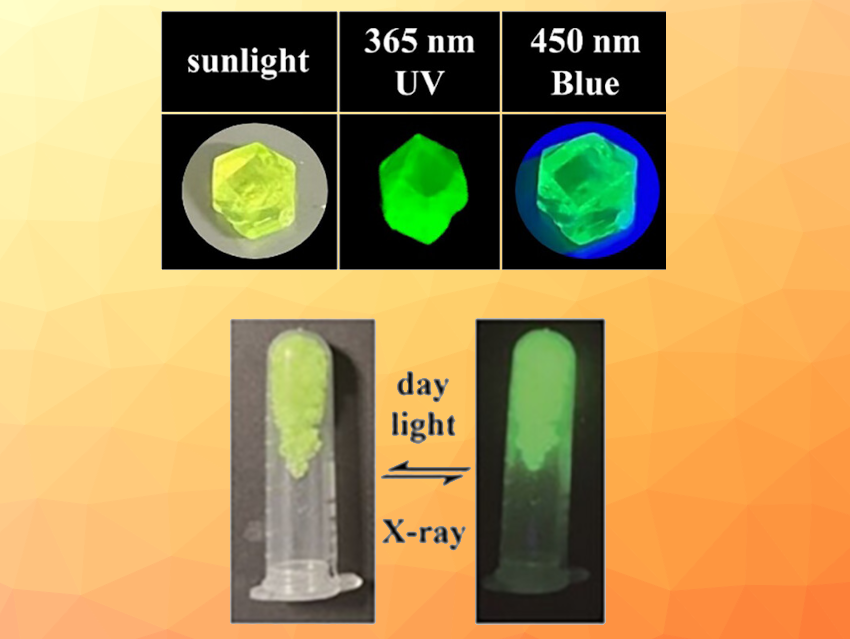
When excited by UV or blue light, the resulting products show strong green light emissions (example pictured) with photoluminescence quantum yields (PLQYs) close to 100 %. Excellent luminescence performance was also observed under X-ray irradiation. The researchers observed a maximum light yield of 80,100 photons/MeV, a minimum detection limit for X-rays that is far lower than the requirement for medical diagnostics, and high X-ray tolerance. These properties, in addition to a short afterglow, allowed the use of the developed materials in high-resolution X-ray imaging.
Overall, the team developed new hybrid manganese halides that show promise as scintillators for advanced applications in X-ray imaging with useful properties such as the absence of toxic lead, simple preparation, high light yields, excellent resolution, and stability.
- Near‐unity broadband emissive hybrid manganese bromides as highly‐efficient radiation scintillators,
Zhongliang Gong, Jie Zhang, Xiangyuan Deng, Meng‐Ping Ren, Wen‐Qi Wang, Yu‐Jiao Wang, Hong Cao, Li Wang, Yuan‐Chun He, Xiao‐Wu Lei,
Aggregate 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.574