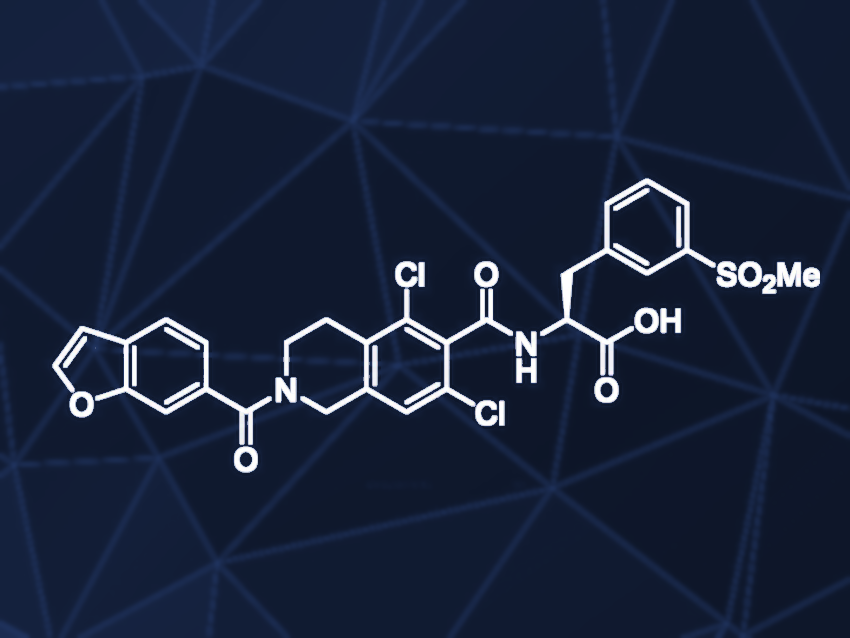
Lifitegrast is a drug approved in 2016 that is used to treat dry eye disease. People suffering from this disease cannot produce enough tears, which leads to inflammation of the eyes and can result in loss of vision if untreated. Lifitegrast is a chiral molecule, and only one enantiomer is used as a therapeutical agent.
Srinivas Achanta, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Hyderabad, India, and colleagues have developed a practical synthesis route for lifitegrast that works without protecting groups or chlorinated solvents and provides the target compound in high yield and purity. In the initial step, an amide coupling was carried out, using 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and hydroxybenzotriazole monohydrate (HOBt). Before addition of the amine, excess coupling reagent was removed to avoid side reactions. The second step consisted of another amide formation with a chiral amino acid, which adds the chiral information to the molecule, leading to lifitegrast dicyclohexylamine salt.
The final step involved the conversion of lifitegrast dicyclohexylamine salt to lifitegrast, using aqueous orthophosphoric acid (OPA) to remove dicyclohexylamine as the corresponding dicyclohexylamine phosphoric acid salt. Lifitegrast was then converted to the corresponding sodium salt, extracted into an aqueous phase, and converted back to the desired product by the addition of aqueous hydrochloric acid. According to the researchers, lifitegrast manufactured via this route complies with the quality guidelines of the International Council for Harmonization (ICH).
- Development of a Practical and Scalable Process for Lifitegrast,
Mahender Madaraboina, Bhimavarapu Srinivasa Reddy, Venkata Siva Kumar Boddupalli, Pavani Sankar Reddy, Jaya Shree Anireddy, Rajeev Rehani Budhdev, Rakeshwar Bandichhor, Srinivas Achanta,
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.3c00228