To ensure that vaccines provide strong and lasting immunization, it is often necessary to supplement the actual vaccine (antigen) with additives that stimulate the immune system: adjuvants. Today, only a few substances have been approved for use as adjuvants.
Glycolipid-Based Adjuvant Library
Carlos A. Guzmán, Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research, Braunschweig, Germany, Daniel G. Rivera, Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry, Halle (Saale), Germany, University of Havana, Cuba, and Finlay Institute of Vaccines, Havana, Cuba, Bernhard Westermann, Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry, and colleagues have introduced a spectrum of new potential adjuvants. They started with the immune stimulant α-galactosyl ceramide (α-GalCer) and synthesized many different variants from a set of four building blocks.
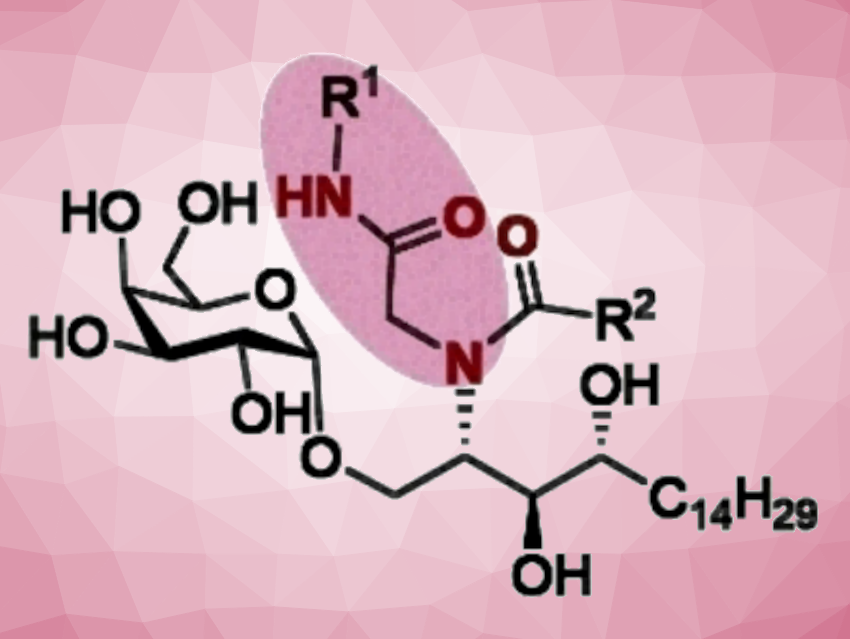
α-GalCer is a synthetic glycolipid (a compound made from fat and sugar building blocks) based on similar compounds found in sea sponges. It binds to CD1d, a special receptor on antigen-presenting cells. This activates certain immune cells and induces the secretion of cytokines that stimulate the immune system. In this way, this substance boosts the immune response, assists in the battle against pathogens and tumor cells, and reduces autoimmune reactions.
Multicomponent Construction and a New Derivatization Hotspot
Among the newly synthesized α-GalCer analogs, the team identified a number of compounds that have significantly better and/or somewhat different activity.
The key to their success was the use of a special reaction for the synthesis of the α-GalCer analogs: in a reaction known as the Ugi four-component reaction, the target molecules are assembled in one step from four individual building blocks. The team varied these four components broadly in a combinatorial method and synthesized a collection of different α-GalCer derivatives.
In particular, the researchers used a functional group that had not been employed in the derivatization of α-GalCer before (the N-substituent of the amide bond, pictured). This allowed the team to introduce many different additional functionalities into their α-GalCer analogs.
Promising Adjuvant Activity
This strategy led to the discovery of compounds that trigger stronger antigen-specific T-cell stimulation and higher antibody reaction when they are administered to mice together with a model antigen, either by injection or through the nasal mucosa. In addition, various functionalized α-GalCer analogs demonstrated stronger adjuvant activity in vitro and in animal studies than an α-GalCer previously optimized (conjugated with polyethylene glycol) for this purpose.
Interestingly, some of the new analogs showed somewhat different effects on the immune system, making it possible to elicit differently balanced immune responses through controlled variation of the derivatization. This could make it possible to develop adjuvants that can be tailored precisely to the requirements of the pathogens in question. In addition, it may be possible to introduce an additional binding site through which the antigen could be bound directly to the adjuvant without compromising its effect—a requirement for the development of self-adjuvating vaccines.
- Diversification of a Novel α‐Galactosyl Ceramide Hotspot Boosts the Adjuvant Properties in Parenteral and Mucosal Vaccines,
Yanira Méndez, Aldrin V. Vasco, Thomas Ebensen, Kai Schulze, Mohammad Yousefi, Mehdi D. Davari, Ludger A. Wessjohann, Carlos A. Guzmán, Daniel G. Rivera, Bernhard Westermann,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202310983