Carbamates are commonly used protecting groups for amines. Available deprotection reactions for these groups are Pd-catalyzed hydrogenolysis or Lewis acid-mediated deprotection with trimethylsilyl iodide. However, these methods can be incompatible with other functional groups, e.g., some nucleophilic sites or sulfur-containing compounds.
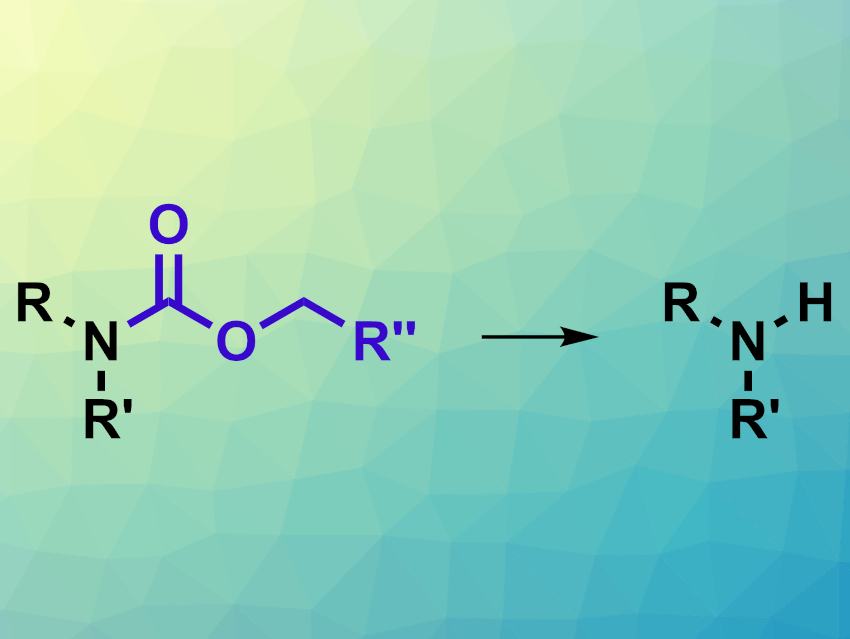
Thomas Scattolin, Mirati Therapeutics, San Diego, CA, USA, and colleagues have developed a method for carbamate deprotection that is complementary to the existing methods and could be an alternative for substrates with incompatible functional groups. In this approach, carbamates are transformed back to the corresponding amines (pictured) via a nucleophilic substitution reaction using 2-mercaptoethanol.
The team deprotected a variety of benzyloxycarbonyl (Cbz)-protected or allyloxycarbonyl (Alloc)-protected amines using two equivalents of 2-mercaptoethanol, K3PO4 as a base, and N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 75 °C.
The desired amines were obtained in generally high yields. The researchers propose that the deprotection proceeds via a nucleophilic attack at the carbon next to the carboxylate, e.g., the benzylic carbon. The protocol shows good functional group tolerance—including, for example, sulfur-containing compounds that can deactivate Pd catalysts.
- A Nucleophilic Deprotection of Carbamate Mediated by 2-Mercaptoethanol,
Thomas Scattolin, Tawfik Gharbaoui, Cheng-Yi Chen,
Org. Lett. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c01410