Test your understanding of industrial safety and the lessons learned from the 2003 West Pharma Services, Inc. incident in Kinston, NC, USA.
In 2003, a buildup of combustible plastic dust at West Pharmaceutical Services ignited, causing a dust explosion and fires that killed six workers and injured 38.
True or False:
A dust explosion occurs when a combustible dust (fuel) is exposed to sufficient heat from an ignition source in the presence of an oxidant (usually the oxygen in air).
See answer
Answer: False
A dust fire, not a dust explosion, occurs when a combustible dust (fuel) is exposed to sufficient heat from an ignition source in the presence of an oxidant (usually the oxygen in air). This is the simple ‘Fire Triangle’.
However, for a dust explosion to occur, the dust must be airborne (i.e., a dust cloud) and in the right concentration (typically at least 30 g/m3), and this dust cloud must be ignited within a confined space. Once ignited, confinement (or congestion) of the combusting dust cloud leads to increased turbulence that causes flame acceleration, that leads to an increase in flame propagation (spread/travel), that in turn leads to an increase in pressure and an accelerated explosion. This is the basis of the ‘Dust Explosion Pentagon’:
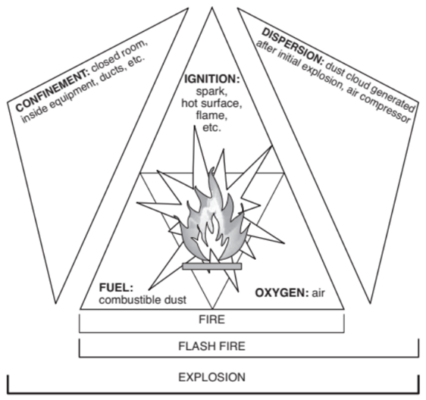
[Image source: National Fire Protection Association (2019). NFPA 652: Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust]
By contrast, as illustrated in the diagram above, in the absence of confinement, ignition of a dust cloud leads to a flash fire.
Which of the following factors increases the risk of dust explosions?
- High humidity
- Dust particle size below 500 μm
- Good ventilation
- Low oxygen concentration
See answer
Answer: 2
Which safety measure could have prevented the West Pharma incident?
- Regular cleaning to prevent dust accumulation
- Avoiding effective ignition sources (such as hot surfaces, electrical equipment, welding, grinding, static discharges, etc.) in areas where dust-producing operations take place
- Containing the spread of dust emissions by sealing off walls, ceilings, and partitions
- Regularly training employees on the hazards of combustible dusts
See answer
Answer: All
Also of Interest

A calendar of process safety incident case studies as a process safety awareness training resource for students and industry

Consequences of electrostatic discharges

Flammable hydrogen-air mixtures

Incompatible mixtures in storage tanks

Hazardousness of high oxygen concentration