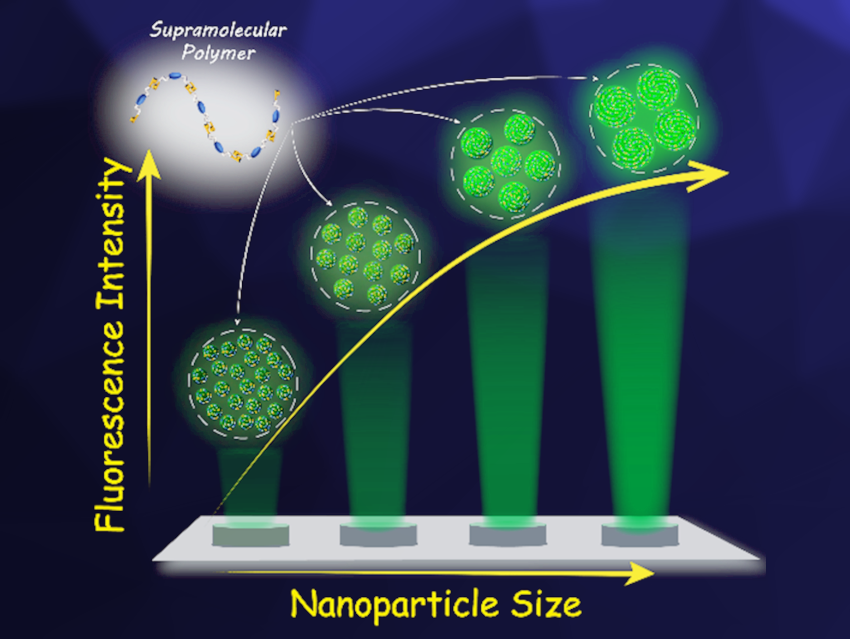
A diverse range of fluorescent nanoparticles, including quantum dots, silicon nanoparticles, carbon dots, and conjugated polymer nanoparticles, have been developed and can be used for imaging and analytical purposes. Establishing a quantitative relationship between the size and the fluorescence of organic fluorescent nanoparticles would be useful for exploring their behavior. However, the prepared organic nanoparticles usually have a broad distribution of sizes, shapes, and defects, which hinders the investigation of size-fluorescence correlations. In addition, organic fluorescent nanoparticles can be affected by aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ), causing a lowered fluorescence signal sensitivity.
Bin Liu, Hui-Qing Peng, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, China, Xiaoyan Zheng, Beijing Institute of Technology, China, and colleagues have performed a quantitative investigation of the size-fluorescence correlation for supramolecular polymeric fluorescent nanoparticles prepared from tetraphenylethylene-based bis-ureidopyrimidinone monomers (bis-UPys). The team used three different monomers to fabricate organic nanoparticles with different sizes. The bis-UPys can assemble into hydrogen-bonded supramolecular polymers for constructing nanoparticles with well-defined shapes, and nanoparticles of different sizes can be easily obtained by adjusting the bis-UPy concentration in the precursor solution. In addition, the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) features of TPE derivatives eliminate the ACQ effect, providing bright fluorescence signals.
The team found a logarithmic relationship between the fluorescence intensity and the size of the fluorescent nanoparticles. They successfully utilized the established fluorescence intensity-size correlation to estimate the sizes of nanoparticles by measuring their fluorescence intensity. The work provides a new way for the simple and real-time determination of nanoparticle dimensions and could be useful for the optimization of size-dependent nanoparticle properties.
- Unveiling size‐fluorescence correlation of organic nanoparticles and its use in nanoparticle size determination,
Wu‐Jie Guo, Shixiang Ma, Hui Wang, Lu Qiao, Lei Chen, Chenyu Hong, Bin Liu, Xiaoyan Zheng, Hui‐Qing Peng,
Aggregate 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.415