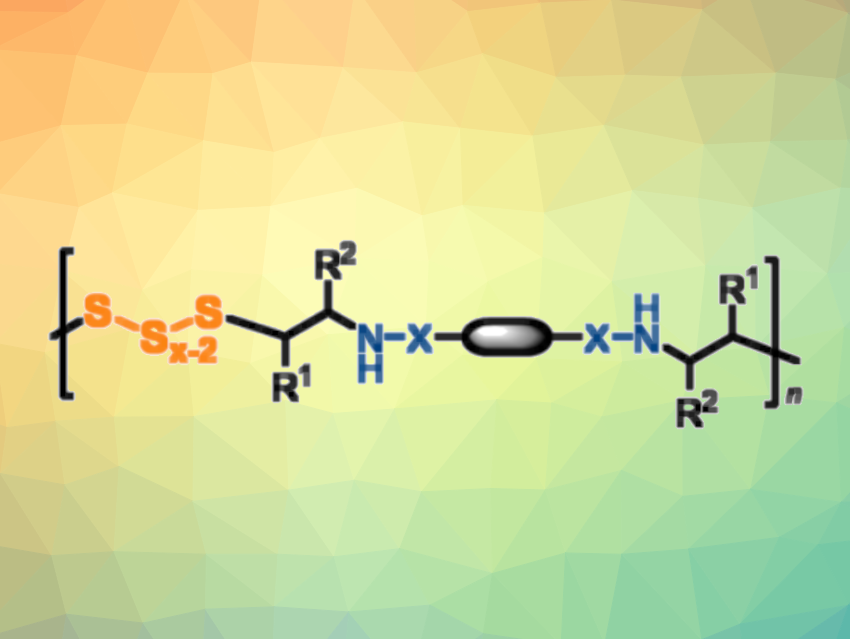
Elemental sulfur is abundant and inexpensive. It is mainly obtained from crude oil refining and natural gas purification, and there is an unused surplus of sulfur that has to be stored. Developing new methods for the use of sulfur in generating valuable compounds and materials would, thus, be useful. One approach to this is the conversion of elemental sulfur into polymer materials. Aziridine, a highly reactive three-membered heterocycle, is interesting for polymer synthesis. However, the bulk radical polymerization of bis(aziridine) with elemental sulfur generates brittle, cross-linked, insoluble polysulfides.
Zhen Zhang, Jinxiang Dong, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, and Guangdong Provincial Laboratory of Chemistry and Fine Chemical Engineering Jieyang Center, Jieyang, China, Nikos Hadjichristidis, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues have synthesized linear polysulfides (pictured) by treating bis(N-sulfonyl/carbonyl) aziridines with elemental sulfur in the presence of an organic base as a catalyst. The reaction features a ring-opening of aziridine with oligosulfide anions, leading to the formation of linear polymers by step-growth polymerization. The team used 7-methyl-1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (MTBD) as the catalyst and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the solvent.
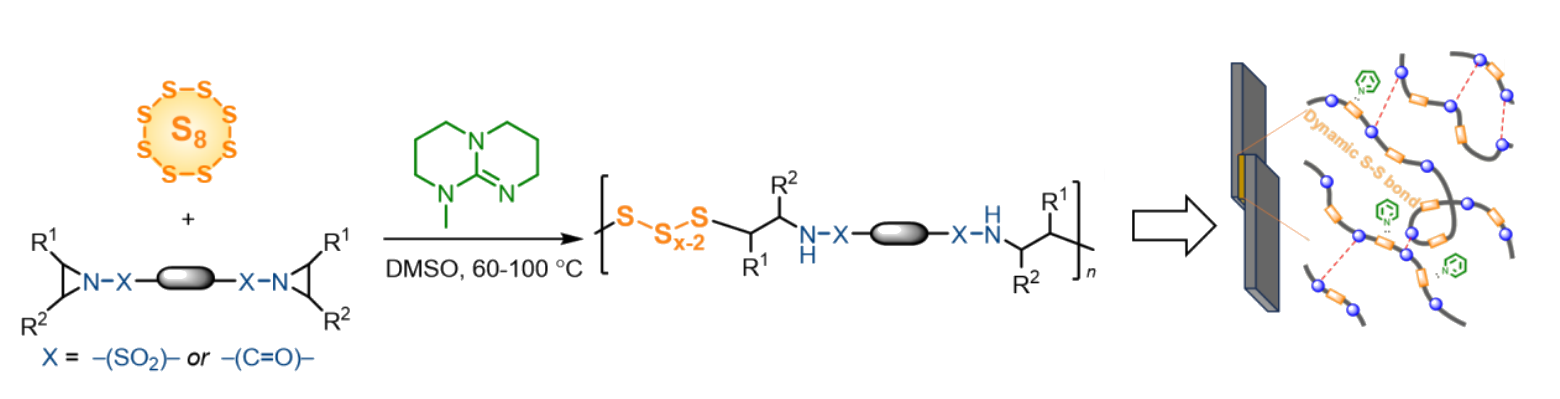
A mixture of the synthesized polysulfides with pyridine exhibits good adhesive properties when applied to, e.g., steel or aluminum substrates. These adhesives show good reusability due to dynamic S–S bonds Overall, the work shows an innovative method for the synthesis of advanced sulfur-containing polymers.
- Step‐growth Polymerization of Aziridines with Elemental Sulfur: Easy Access to Linear Polysulfides and Their Use as Recyclable Adhesives,
Huishan Huang, Shuojia Zheng, Jiye Luo, Liang Gao, Yanxiong Fang, Zhen Zhang, Jinxiang Dong, Nikos Hadjichristidis,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202318919