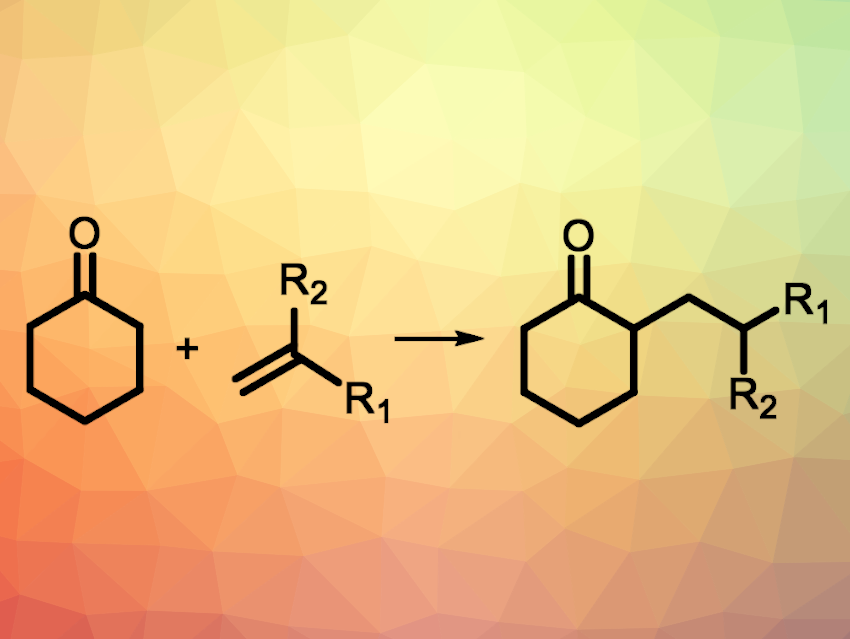
Ketones are common functional groups, e.g., in bioactive natural products and synthetic pharmaceutically active compounds. The C−H functionalization of ketones is, thus, an interesting research target. Organocatalysts based on amines can be used to activate C−H bonds of ketones, but the activation of the α-C‒H bond typically requires an amine and a directing group to guide the reaction.
Li-Zhu Wu, Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing, and colleagues have developed the first α-alkylation of cyclic ketones in the absence of amine catalysts and directing groups (example reaction pictured). The team used CdSe quantum dots (QDs) as a photocatalyst to activate the α-C–H bond of ketones. The ketone substrates were reacted with a variety of 1,1-diphenylethene derivatives (or other chain-terminal olefins) in the presence of the quantum dots and K2HPO4 or DMAP as a base under blue LED irradiation. The reactions were performed at room temperature under an argon atmosphere.
The desired α-alkylation products were obtained in moderate to excellent yields. According to the researchers, the ketones are adsorbed on the surface of the quantum dots, binding via the carbonyl group. A radical is then formed at the neighboring α-carbon under light irradiation via a selective activation of the α-C–H bond. Finally, the radical is coupled with the alkene reaction partner.
- Amine‐Free, Directing‐Group‐Free and Redox‐Neutral α‐Alkylation of Saturated Cyclic Ketones,
Jia Qiao, Rui-Nan Ci, Qi-Chao Gan, Cheng Huang, Zan Liu, Hui-Lan Hu, Chen Ye, Bin Chen, Chen-Ho Tung, Li-Zhu Wu,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202305679