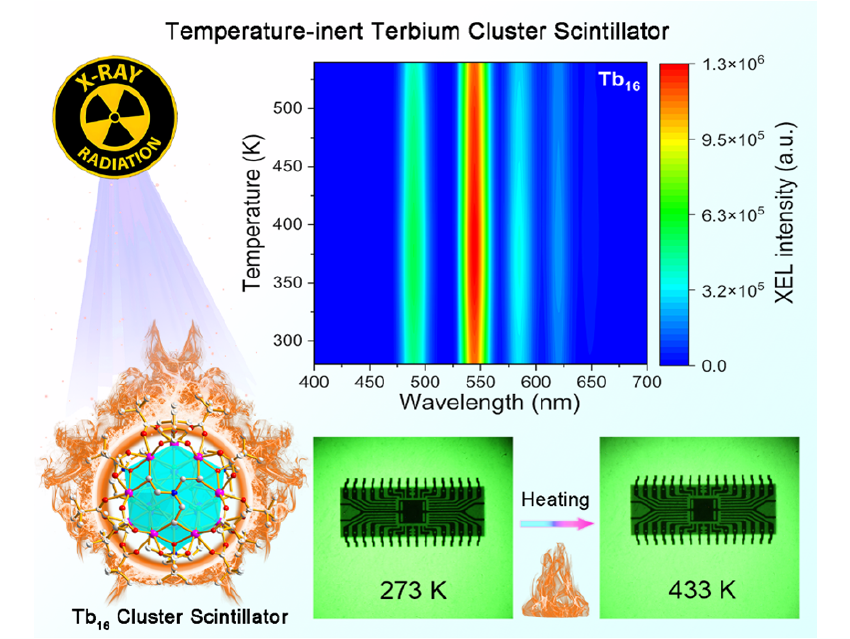
X-ray scintillators play a critical role in medical diagnostics and industrial applications by converting ionizing radiation into low-energy photons. However, similar to most luminescent materials, the emission intensity of scintillators is typically affected by ambient temperature. A rise in temperature generally leads to a sharp decline in radioluminescence. These characteristics limit the application of scintillators under extreme conditions. To date, temperature-inert metal cluster scintillators have been rarely reported due to the lack of effective design strategies.
Kai Li and Shuang-Quan Zang, Zhengzhou University, Henan Province, China, and colleagues proposed a comprehensive design strategy combining triplet exciton recycling and fluoride-bridge-induced carrier traps for the development of a temperature-inert cluster scintillator (Tb₁₆; Tb₁₆(µ₄‑F)₆(µ₃‑F)₁₂(tBuCOO)₁₈[N(CH₂CH₂O)₃]₄. The Tb₁₆ cluster exhibits remarkable stability in radioluminescence intensity over a broad temperature range of 300 K to 540 K. Mechanistic studies show that high-efficiency triplet exciton recycling in Tb₁₆ endows it with intense radioluminescence, while carrier traps induced by fluoride-bridge structures efficiently capture charge carriers at low temperatures and release them back to the excited state at high temperatures, compensating for emission loss.
Tb₁₆-PVDF scintillator screen was further prepared, which shows excellent stability. The Tb₁₆-PVDF scintillator screen is a composite material in which Tb₁₆, a terbium-based metal cluster scintillator, is embedded or dispersed within PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), a polymer matrix. High-resolution, variable-temperature X-ray imaging of standard line-pair mask and electronic components was successfully demonstrated using the Tb₁₆-PVDF scintillator.
- Temperature-inert Terbium Cluster Scintillator
You-Song Hu, Ruo-Yu Fang, Yan-Hao Liu, Meng-Han Fu, Shu-Han Wang, Jia-Wang Yuan, Qi Yang, Qiu-Chen Peng, Zhao-Yang Wang, Xiu-Qin Li, Kai Li, Shuang-Quan Zang,
Aggregate 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70140