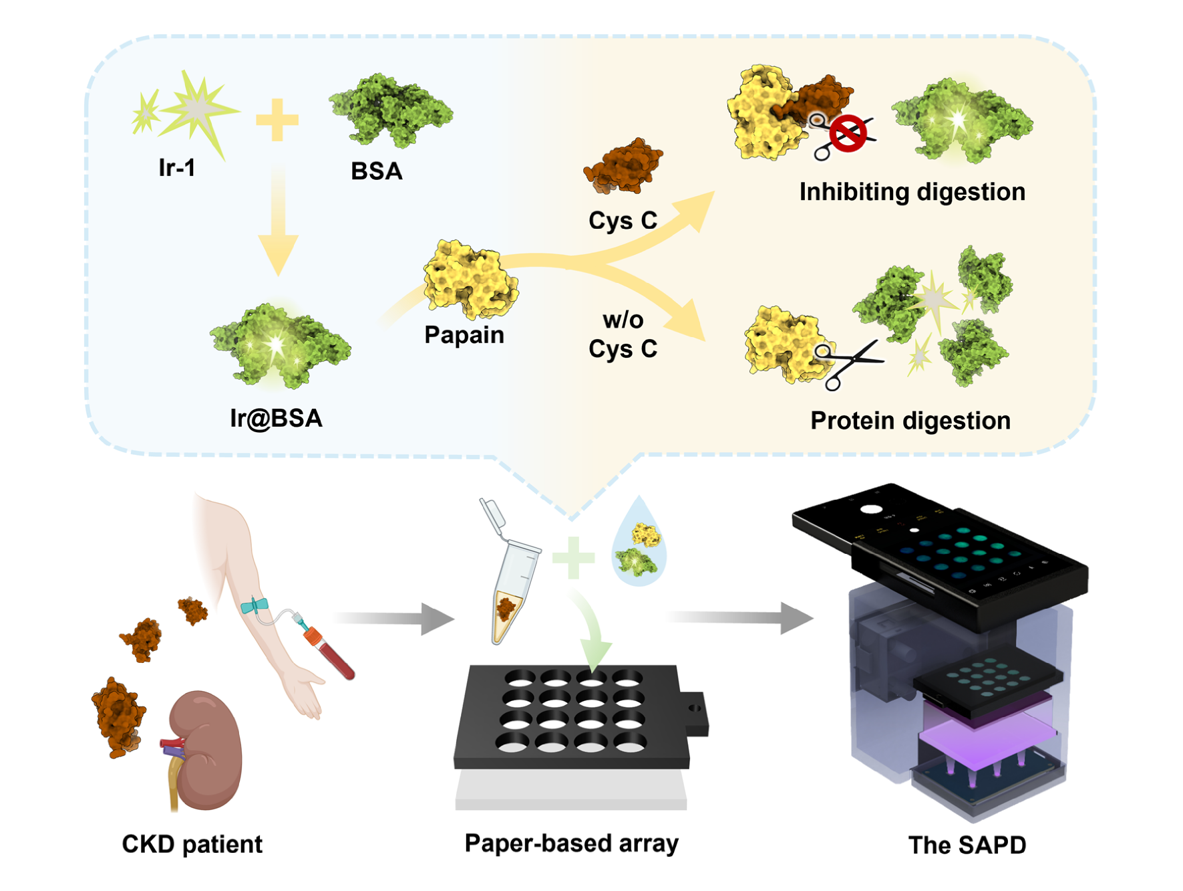
The development of affordable, user-friendly diagnostic tools for early warning and monitoring of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is crucial to reducing CKD-related morbidity and mortality. Recently, smartphones have emerged as a promising option for point-of-care testing (POCT), circumventing the need for large, specialized, and complex instruments. However, because smartphone-based optical devices typically rely on cost-effective but low-performance hardware, developing sensing schemes with robust and stable optical signals to meet the sensitivity requirements of diverse POCT applications remains challenging.
Changqing Yi (Sun Yat-Sen University), Meijin Li (Fuzhou University), and Zhaofan Luo (Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University) reported:
- a protein-templated AIEgen, Ir@BSA, which emits intense green phosphorescence with a quantum yield up to 69.40% and a lifetime up to 1839.40 ns in aqueous solution;
- a straightforward protocol for cystatin C (Cys C) quantitation employing Ir@BSA as the phosphorescent signal indicator and papain as the biomolecular recognition element; and
- a smartphone-based portable phosphorescence reader (SAPD) capable of stably exciting and accurately collecting phosphorescence signals from paper-based arrays.
Quantitation of Cys C in clinical serum samples using SAPD integrated with the paper-based arrays demonstrated high sensitivity (0.36 μg mL⁻¹) and specificity, cost-effectiveness (~67.5 USD per set), portability (~450 g), good precision (RSD ≤ 8.25%), good accuracy (comparable to the clinical standard latex immune-turbidimetric method), and high throughput (16 samples per experiment). Importantly, this study highlights the significant potential of Cys C as an early warning marker of CKD progression. The reported method enables Cys C quantitation anywhere, anytime, by anyone, and is ideally suited for mass CKD screening and home monitoring, facilitating early diagnosis and proactive disease management.
- AIEgen-based and smartphone-assisted on-site quantitation of cystatin C for monitoring of chronic kidney disease
Shuqi Xia, Xue Zhu, Shiqiong Niu, Wanqing Zhang, Jinyi Gong, Zhaofan Luo, MeiJin Li, Changqing Yi
Aggregate 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70127