Researchers develop bright, stable organic dyes that enable precise deep-tissue imaging and disease detection in the NIR-IIx spectrum
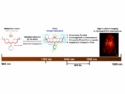

Researchers develop bright, stable organic dyes that enable precise deep-tissue imaging and disease detection in the NIR-IIx spectrum
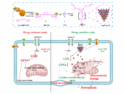
A natural nanocomplex overcomes drug resistance in liver cancer by inducing ferroptosis through a three-part mechanism that reduces glutathione in cancer cells, weakening their antioxidant defenses and causing cell death
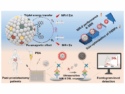
A luminescent nanoparticle assay enables ultra-sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen for early diagnosis and recurrence monitoring
![Diazine-Tetraphenylethylene Cyclo[6]arenes for Molecular Recognition in Solution and Aggregate States](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/ChemistryViews-2.70171-125x94.png)
1,2-diazine endo-functionalized tetraphenylethylene cyclo[6]arenes for cation binding in dilute solution and nitrophenol detection in the aggregate state

By precise molar ratio control strategy, tricolor carbon dots with high quantum yields are prepared for integrated lighting–energy applications
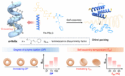
Chain length and self-assembly temperature of α-helix controls aqueous circularly polarized luminescence in homopolypeptide self-assembly
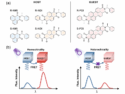
Förster resonance energy transfer enables efficient, noncovalent chiral recognition in solid-state systems when host and guest share the same chirality
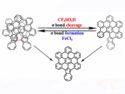
Covalent bond regulation controls azulene-mediated nanographene aggregation via acids, while quenchers and temperature dictate product selectivity

Organic nanoparticles reversibly self-assemble and show fatigue-resistant fluorescence modulation, offering new opportunities for smart optoelectronics
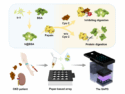
Cost-effective smartphone phosphorescence detection of cystatin C supports early warning and proactive care in chronic kidney disease