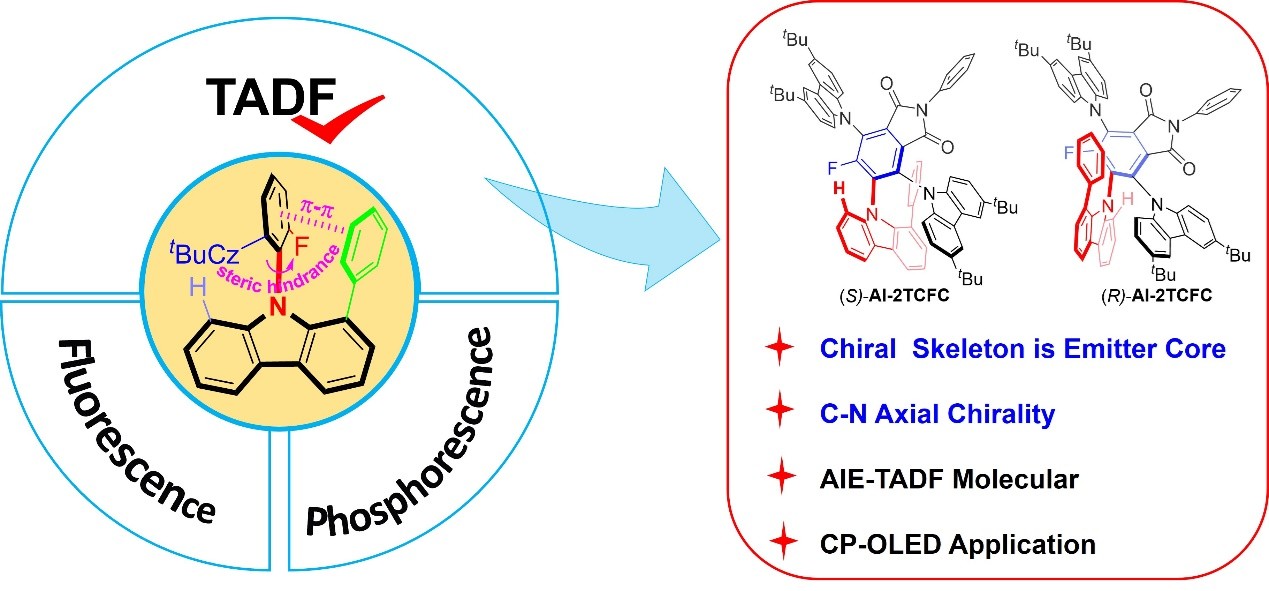
In the realm of optical materials, circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) materials have garnered substantial attention due to their immense potential in applications such as optoelectronic devices and 3D displays. However, the design of highly efficient chiral frameworks remains a formidable challenge. To expand the repertoire of chiral frameworks for CPL materials, the authors propose an innovative chiral strategy centered on the carbon–nitrogen (C-N) axial chirality. This approach offers novel insights into addressing the issue of separation between the chiral framework and the chromophore, thereby enriching the diversity of CPL materials.
Ben Zhong Tang, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen), China, and colleagues designed and synthesized a pair of enantiomers based on C-N axially chiral, (S/R)-AI-2TCFC, featuring a core structure composed of the classic carbazole chromophore and an imide acceptor. This molecular design not only retains the excellent luminescent properties of carbazole but also enables chiral expression through C-N axial chirality. The molecules exhibit typical aggregation-induced emission (AIE) and thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) characteristics, with an emission peak at 578 nm in both toluene solution and neat film states, and possess a luminescence dissymmetry factor (glum) on the order of 10−3. Single-crystal structure analysis confirmed the absolute configuration of the C-N axial chirality and revealed the significant contribution of steric hindrance and intramolecular π-π interactions to the stabilization of the axial chirality.
Circularly polarized electroluminescence (CPEL) devices based on these molecules demonstrated satisfactory electroluminescence performance, providing important insights for the development of high-performance CPL materials based on C-N axial chirality in the future.
- Carbon–Nitrogen Axial Chirality as a Novel Chiral Framework Design Strategy for Circularly Polarized Luminescence Materials
Lei Zeng, Chen-Hao Guo, Chensen Li, Ziwei Deng, Yi Lu, Lin Lu, Peng Meng, Shuaijun Sun, Zijie Qiu, Meng Li, Yu Xiong, Zheng Zhao, Chuan-Feng Chen, Ben Zhong Tang
Aggregate 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70069