The transition metal (TM)-free oxidative cross-coupling of C–H bonds is an atom-economical approach for the construction of C–C bonds, which avoids expensive metal catalysts, ligands, pre-functionalized substrates, and additional steps. 3-Substituted and 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles are prominent structural motifs in many biologically active products and pharmaceuticals. Generally, the synthesis of 3-substituted indoles requires pre-functionalized coupling partners and heavy transition-metal catalysts, as well as high temperatures.
Sangit Kumar, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India, and colleagues have developed a TM- and halogen-free, NaOtBu–mediated selective oxidative cross-coupling between oxindoles and nitroarenes to access 3-aryl substituted and 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles at room temperature. The oxindole was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and combined with nitrobenzene and NaOtBu to give the desired product. The method tolerates a wide range of functional groups on the nitroarene.
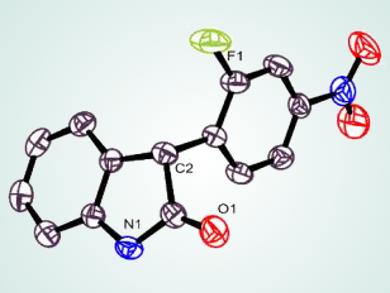
Interestingly, styrene derivatives were also reactive under TM-free conditions at ambient temperature, forming quaternary 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles. These 3-(nitroaryl)-oxindoles (pictured) can be transformed into advanced heterocycles such as benzofuroindoles, indoloindoles, and substituted indoles by taking advantage of their versatile nitro group.
- Transition-Metal-Free Chemoselective Oxidative C-C Coupling of sp3 C-H Bond of Oxindoles with Arenes and Addition to Alkene: Synthesis of 3-Aryl Oxindoles, Benzofuro- and Indoloindoles,
Sangit Kumar, Moh. Sattar, Vandana Rathore, Ch. Durga Prasad,
Chem. Asian J. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/asia.201601647