DNA-alkylating drugs used in cancer therapy cause DNA damage, which leads to the formation of abasic sites (AP sites = apurinic/apyrimidinic sites). However, these sites are largely eliminated by the base excision DNA repair (BER) pathway, based on the action of a key enzyme, APE1. This enzyme was linked to radio- and chemoresistance in certain cancers. APE1 is currently considered as an important drug target for the improvement of anti-cancer treatment.
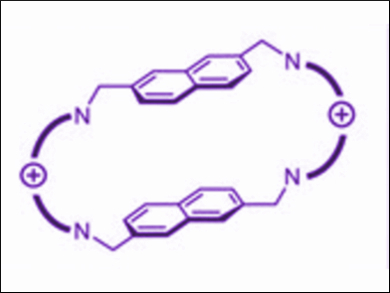
Anton Granzhan, Institut Curie, PSL Research University, and Université Paris-Saclay, both Orsay, France, and colleagues are pursuing an alternative strategy that, instead of targeting APE1 enzyme, rather relies on targeting its substrate: AP sites in DNA. The team synthesized and studied a new generation of AP-site ligands, which share a common cyclophane scaffold but bear a variety of substituents (scaffold pictured above). The ligands are based on a 2,7-naphthalenophane scaffold and were prepared from the common starting material 2,7-bis(bromomethyl)naphthalene.
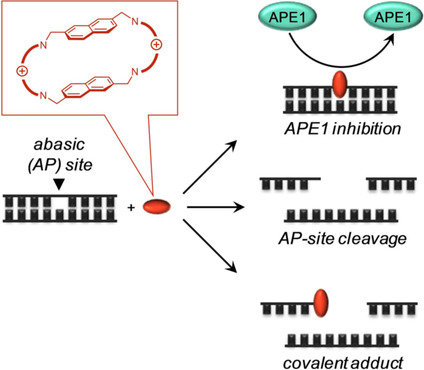
The results demonstrate that most ligands strongly and selectively bind to AP-sites in DNA (pictured below, top right) and inhibit APE1 activity in vitro, with inhibitory constants in the nanomolar range. Additionally, they found that the ligands have an intrinsic AP-site cleavage activity (pictured below, center right). This cleavage has a mechanism different from that of APE1, and its efficiency could be modulated by the molecular design of ligands. Finally, they also observed the formation of an unprecedented DNA–ligand adduct with one of the tested ligands (pictured below, bottom right). The researchers believe that new ligands interacting with AP-sites could modulate DNA repair pathways in multiple ways, and eventually improve the efficiency of the DNA-alkylating drugs.
- Interaction of Functionalized Naphthalenophanes with Abasic Sites in DNA: DNA Cleavage, DNA Cleavage Inhibition, and Formation of Ligand–DNA Adducts,
Coralie Caron, Xuan N. T. Duong, Régis Guillot, Sophie Bombard, Anton Granzhan,
Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1949–1962.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201805555