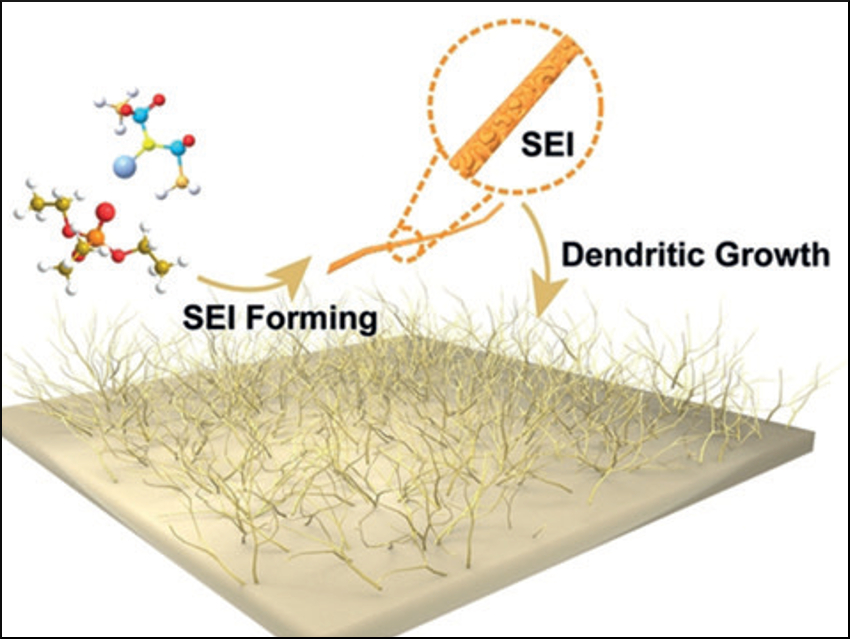
High-energy-density lithium-metal batteries are susceptible to dendrite formation, which can cause short circuits and thus, heat. In the presence of a flammable battery electrolyte, fires or explosions can occur. Electrolytes that use flame-retardant solvents, such as organic phosphate electrolytes (OPEs), could eliminate fire hazards and ensure safer working batteries.
Yu-Guo Guo, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and colleagues have developed a Li-metal battery containing a lithium nitrate additive, which is compatible with the flame-retarding electrolyte triethyl phosphate. The researchers investigated the lithium-plating process at the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) using scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy.
In the presence of the additive, lithium was deposited uniformly at the Li-metal anode and dendrite formation was avoided—even at a high 16 mA cm–2 current density. The homogeneous Li/electrolyte interface has a low resistance and allows a working battery to function with a higher Coulombic efficiency and a longer cycling life compared with an additive-free cell.
- Nitriding-Interface-Regulated Lithium Plating Enables Flame-Retardant Electrolytes for High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries,
Shuang-Jie Tan, Junpei Yue, Xin-Cheng Hu, Zhen-Zhen Shen, Wen-Peng Wang, Jin-Yi Li, Tong-Tong Zuo, Hui Duan, Yao Xiao, Ya-Xia Yin, Rui Wen, Yu-Guo Guo,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7802–7807.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201903466