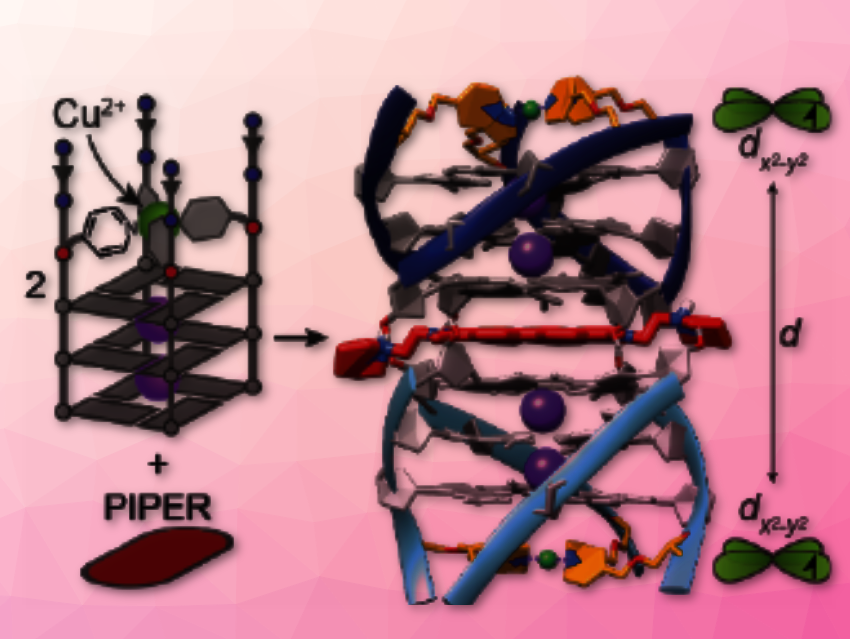
Human DNA usually adopts a helical, double-stranded structure. However, four-stranded variants, so-called G quadruplexes, are also possible. They form from guanine-rich sequences that resemble columnar stacks and they can bind small molecules in between them forming sandwich-like complexes held together by non-covalent interactions. G-quadruplexes play a crucial role in diseases such as cancer, and as they easily form higher-order structures such as pairs (“dimers”) and bind small molecules, they are promising drug candidates. Elucidation of their structure in solution is challenging.
Guido H. Clever, Müge Kasanmascheff, TU Dortmund University, Germany, and colleagues have developed a method for the precise distance measurement in pairs of G-quadruplexes with or without bound drug-like molecules using EPR spectroscopy. With this method, the structure of such DNA adducts can be elucidated with high accuracy. It also provides information on intercalated compounds.
DNA G-quadruplexes were chemically modified to incorporate copper ions that are tightly held in place in a rigid environment. The team could then demonstrate the formation of dimers and sandwiches by measuring distances between the copper ions.
The researchers were able to demonstrate the intercalation of G-quadruplex-binding ligands such as PIPER (N,N’-bis[2-(1-piperidino)ethyl]-3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide dihydrochloride) and telomestatin, thereby uncovering previously undescribed binding modes. They could also show that unbound G-quartets consisting of free guanines or guanosines intercalate into G-quadruplex dimers and form sandwich structures.
According to the researchers, the developed tool will help to find new DNA-binding molecules and measure other biologically relevant DNA interactions.
- Precise Distance Measurements in DNA G‐Quadruplex Dimers and Sandwich Complexes by Pulsed Dipolar EPR Spectroscopy,
Lukas M. Stratmann, Yury Kutin, Müge Kasanmascheff, Guido H. Clever,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202008618
Update (November 24, 2020)
The text originally omitted Müge Kasanmascheff as a corresponding author of the covered research article.