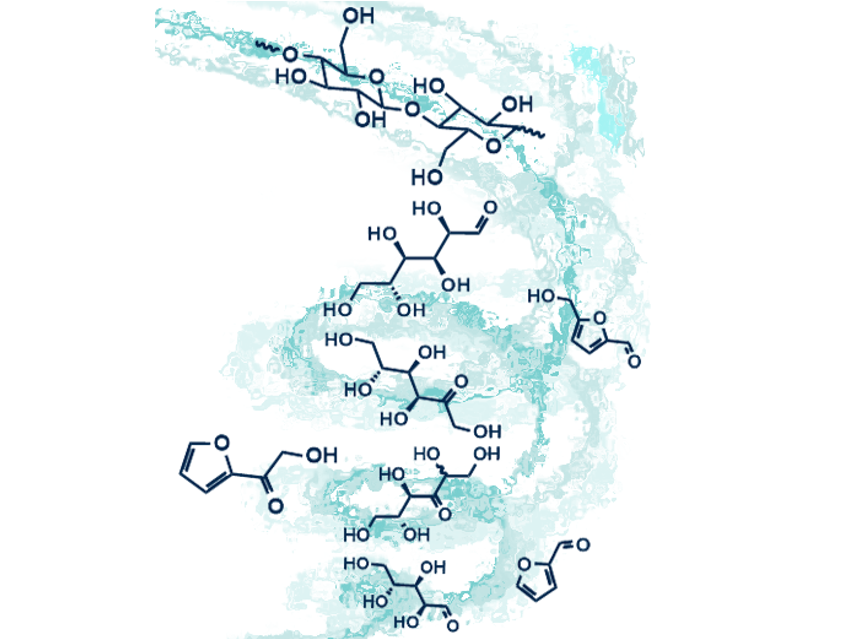
Cellulose is plentiful, is present in many existing undervalued or waste streams, and already has a massive industry related to its processing. It is a bioresource with immense potential to replace substantial volumes of petrochemicals. But its processing into platform chemicals is difficult. Ionic liquids have been used extensively as media for reactions of cellulose. Among ionic liquids, zinc chloride hydrate is less well-represented despite its many excellent physical and chemical characteristics. Furan derivatives, which are used in plastics, can be produced from cellulose in acid-catalyzed transformations, but these furanoids are susceptible to by-product formation under the acidic conditions employed.
Bradley Williams and colleagues, The University of Technology Sydney, Australia, have investigated the use of zinc chloride hydrate, which is usually represented as ZnCl2•nH2O, is a true ionic liquid known for its highly acidic nature, and is more accurately represented as [Zn(OH2)6][ZnCl4]. They used zinc chloride hydrate as reactive solvent to dissolve cellulose and to cause its acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, its isomerization into fructose, and dehydration into furyl hydroxymethyl ketone and furfural as major products. Within the series ZnCl2•3H2O, ZnCl2•3.25H2O, and ZnCl2•3.5H2O, the researchers established that ZnCl2•3H2O afforded optimum yields and selectivities.
Key to success in this chemistry is the use of anisole as extracting solvent to ensure separation of the furanoids from the acidic medium. Optimized reaction conditions enable the production of the furanoids in excellent yields of up to 46 %, giving a glimpse of the growing promise of this type of approach to find sustainable replacement products for petrochemicals.
- Acid-Catalysed Conversion of Carbohydrates into Furan-Type Molecules in Zinc Chloride Hydrate,
Iurii Bodachivskyi, Unnikrishnan Kuzhiumparambil, D. Bradley G. Williams,
ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 352–357.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201800650



Good article on adding value to agricultural waste. Can other acids be used like, aluminium chloride, zeolites etc.?