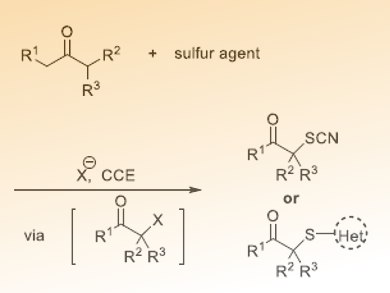
Sulfur-containing compounds are important building blocks in the pharmaceutical industry and material science. Although many methods have been developed to form C–S bonds, transition metals or excess external oxidants are usually needed. To find an efficient, green, and sustainable method is still a challenging task.
Chen-Chu Zeng and Bao-Guo Sun, Beijing Technology and Business University and Beijing University of Technology, China, and colleagues have developed a protocol to electrochemically synthesis α-thiocyanated and α-sulfenylated ketones using redox-active NaI/heterogeneous solid acid Amberlyst-15(H) dual catalysts system in a simple undivided cell. The reactions are carried out in a mixed solvent of EtOH/DMSO/H2O using graphite plate anode and cathode, connected to a DC regulated power supply. The mixture of the reactants is electrolyzed under constant current conditions at 4 mA/cm2 at 70 °C and the electrolysis is terminated when 15 F/mol of charge have been consumed.
The reaction tolerates a wide range of functional groups and could be used in gram scale synthesis. The researchers suggest that the reaction involves an initial α-iodination and a subsequent nucleophilic substitution with NaSCN or heterocyclic thiols.
- Redox-active sodium iodide/recyclable heterogeneous solid acid: An efficient dual catalytic system for electrochemically oxidative α-C-H thiocyanation and sulfenylation of ketones,
Sen Liang, Cheng-Chu Zeng, Hongyu Tian, Baoguo Sun, Xugang Luo, Fazheng Ren,
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201701401