C–H carboxylations using carbon dioxide are challenging due to the low reactivity of CO2. There are some transition-metal-catalyzed methods for this type of transformation, but a direct carboxylation of the aryl C–H bonds of amine derivatives had not been achieved so far.
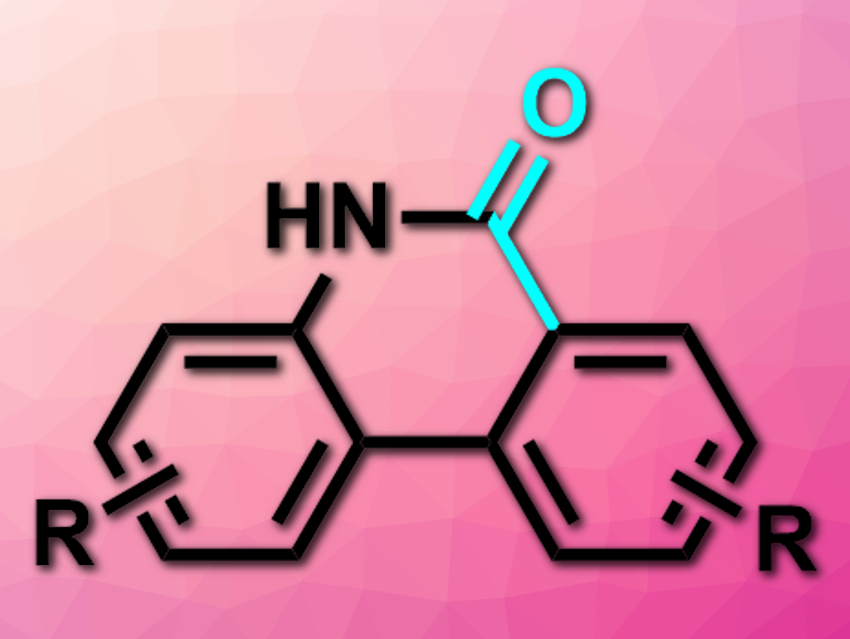
Gang Li, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter and State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, both Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fujian, China, and colleagues have developed a direct, Rh(I)-catalyzed, amino-group-assisted C–H carboxylation of 2-arylanilines with CO2. The team used [RhCl(cod)]2 (cod =nbsp;1,5-cyclooctadiene) as a catalyst, a triarylphosphine as a ligand, tBuOK as a base, and dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent to convert different 2-arylanilines and 2-heteroarylanilines to phenanthridinone derivatives (pictured).
The desired products were obtained in good to excellent yields. The team proposes a mechanism that involves the oxidative of the RhI species to the C–H bond, the reductive elimination of the hydrogen, and the nucleophilic addition of CO2 to the resulting rhodacycle intermediate. A final base-mediated lactamization then gives the product.
- Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Aryl C–H Carboxylation of 2-Arylanilines with CO2,
Yuzhen Gao, Zhihua Cai, Shangda Li, Gang Li,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01105