Phosphorus-containing organic compounds are useful in, e.g., catalysis and medicinal, or agricultural chemistry. They can, for example, be synthesized via C–H phosphorylation reactions using transition-metal or photoredox catalysis. However, avoiding the use of expensive transition metals or stoichiometric redox reagents is challenging.
Ping-Hua Sun, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, Zhixiong Ruan, Guangzhou Medical University, China, and colleagues have developed an electrochemical phosphorylation of aldehyde hydrazones that needs no external oxidants. The team used aryl- or- alkyl-substituted aldehyde hydrazones and diphenylphosphine oxide (HPh2P=O) as substrates and electrolyzed them at a constant current in a solution of NEt4ClO4 in MeCN with a catalytic amount of MnBr2·4H2O. The electrolysis was performed at room temperature under atmospheric conditions using a simple, undivided cell with a graphite anode and a platinum cathode.
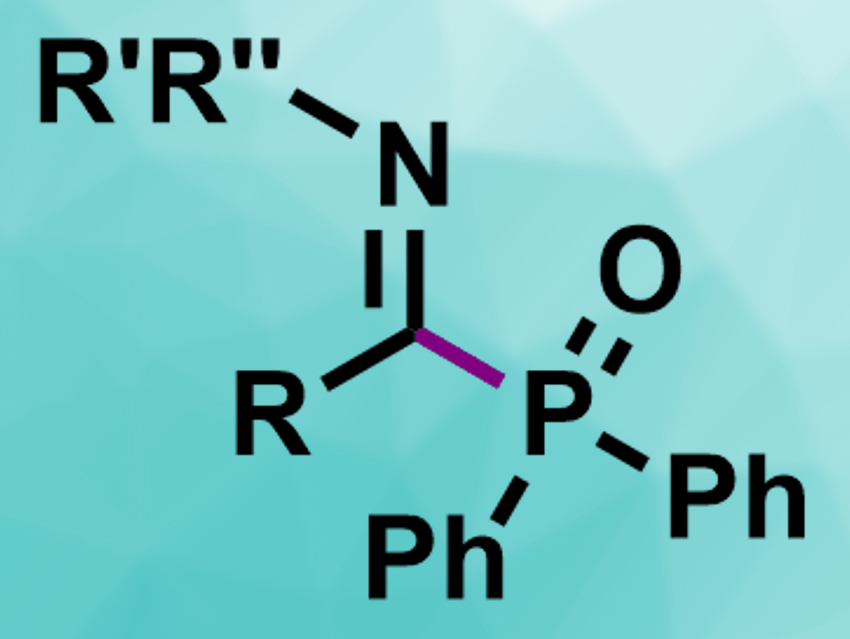
The desired α-iminophosphine oxides (pictured) were obtained in moderate to excellent yields. The reaction tolerates different N-substituents at the hydrazone and a range of functionalized aryl groups at the phosphine oxide. It is simple to perform and can be used on a gram scale.
- Electrochemical Oxidative Phosphorylation of Aldehyde Hydrazones,
Zhongnan Xu, Yueheng Li, Guangquan Mo, Yucheng Zheng, Shaogao Zeng, Ping-Hua Sun, Zhixiong Ruan,
Org. Lett. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01343