Cyclosporin A is a calcineurin inhibitor used for suppressing the immune system during organ transplantation and in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. It works by inhibiting a family of transcription factors called NFATs, which are important for T-cell development and function. However, NFATs’ effects on other cell types involved in the innate immune response had not yet been elucidated.
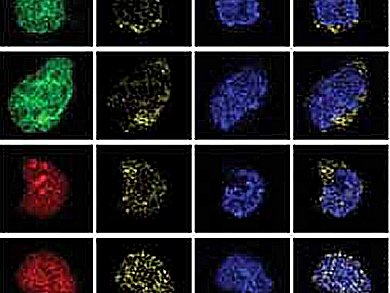
Jan Fric, A*STAR Singapore Immunology Network, Singapore, and co-workers have shown that in addition to promoting T-cell development, NFATs also suppress the maturation of myeloid cells. Myeloid cells provide the body’s first line of immune defence, as it is their job to detect and eliminate pathogens.
NFAT negatively regulates myeloid expansion by suppressing the transcription of essential cell cycle genes. Inhibiting NFAT relieves this suppression and allows myeloid cells to progress more rapidly through the cell cycle, resulting in an expansion of the myeloid cell population.
These findings can help to better understand the drug’s side effects, and eventually, long term further research can lead to therapy modifications.
- Calcineurin/NFAT signalling inhibits myeloid haematopoiesis,
Jan Fric, Clarice X. F. Lim, Esther G. L. Koh, Benjamin Hofmann, Jinmiao Chen, Hock Soon Tay, Siti Aminah Bte Mohammad Isa, Alessandra Mortellaro, Christiane Ruedl, Paola Ricciardi-Castagnoli,
EMBO Molecular Medicine 2012, 4 (4), 269–282.
DOI: 10.1002/emmm.201100207
EMBO Molecular Medicine, one of the highest cited journals in the biomedical sciences, is now a fully Open Access journal.