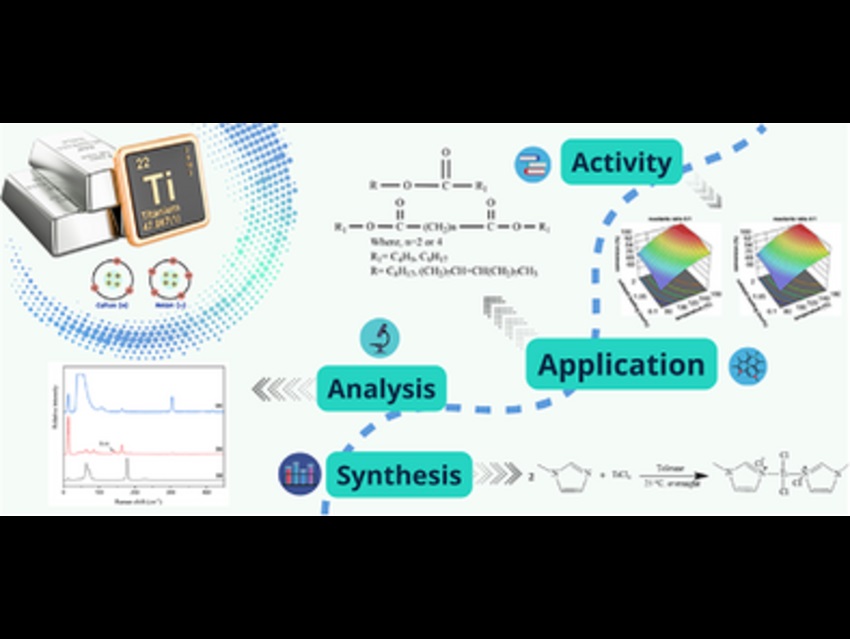
Oleic acid esterification is important for producing eco-friendly chemicals like biodiesel and other oleic acid-based esters, which are used in various applications like lubricants and cosmetics. Traditional catalysts often lack efficiency or stability. This study aims to develop a better-performing, sustainable catalyst for this reaction.
The research was carried out by a team including Piotr Latos, Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice, Poland, Sebastian Jurczyk, Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice, Poland, and colleagues. The team synthesized hybrid catalysts by reacting titanium tetrachloride (TiCl₄) with 1-methylimidazole (Im) in varying molar ratios (1:1 to 1:4), and the resulting materials were thoroughly characterized using XRF, TEM, NMR, Raman, and FT-IR techniques. The most efficient catalyst, a TiCl₄/Im hybrid with a 1:2 ratio, was investigated in the esterification of oleic acid with 2-ethylhexanol under optimized conditions: 0.5 mol% catalyst loading, a reactant ratio of 1:2, at 140°C for 3 hours. The reaction yielded a high conversion rate of 96%, with the catalyst demonstrating strong stability and low titanium leaching across multiple cycles. This makes it a promising candidate for green and scalable esterification processes.
This catalyst could be a sustainable alternative for industrial esterification, especially in biodiesel production. Its high efficiency, low toxicity, and reusability make it suitable for scaling up. Future work may explore similar hybrid systems for other green chemical transformations.
-
-
- Tailored Imidazolium-Titanium Catalyst for Enhanced Oleic Acid Esterification,
Lema Deme Shumi, Piotr Latos, Sebastian Jurczyk, Dariusz Łukowiec, Paweł M. Nuckowski, Sebastian J. Balicki, Kazimiera A. Wilk, Anna Chrobok, ChemCatChem 2025.
-