The synthesis of cyclic compounds is a very common task in organic chemistry. While the preparation of five- or six-membered rings is commonplace, seven-membered rings can be more challenging to access. Nevertheless, cycloheptane-based structural units are often found, e.g., in natural products or pharmaceutically active compounds. One approach to the synthesis of cyclic systems is the use of electrocyclization reactions. The electrocyclization of heptatrienyl anions, for example, has long been known, but is not often used in synthesis due to a need for harsh conditions and limitations in substrate scope.
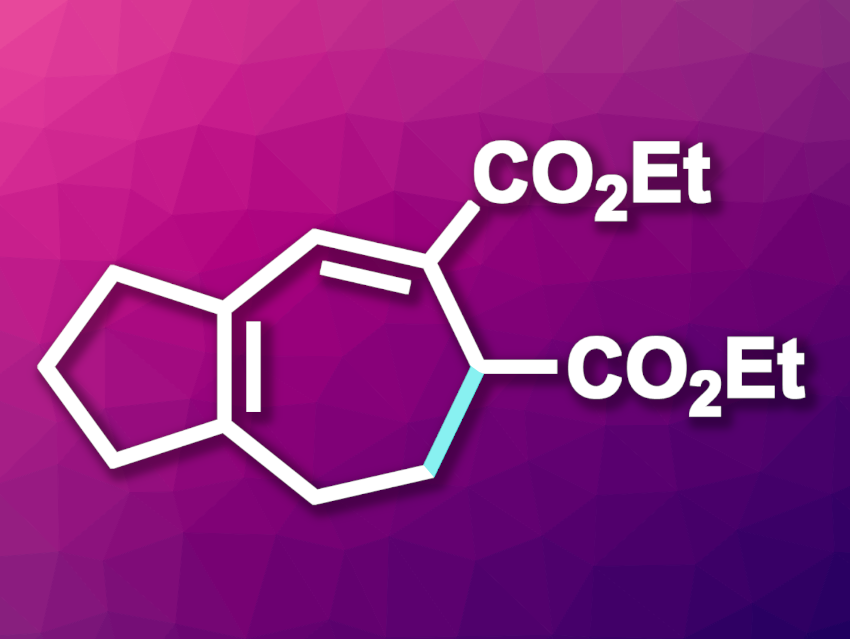
Arturo Orellana, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada, and colleagues have developed an approach to the electrocyclization of heptatrienyl anions under mild conditions to give functionalized cycloheptanes (example product pictured). The team prepared trienes from cyclopentanone or ortho-bromobenzaldehydes and subjected them to electrolysis at room temperature in the presence of 1,8-diazabicyclo(5.4.0)undec-7-ene (DBU) as a base, using dimethyl sulfoxide as the solvent.
Under these conditions, the desired cycloheptanes were obtained in yields of up to 95 %. For some substrates, even catalytic amounts of DBU provided high yields. According to the researchers, the developed approach shows the mildest conditions ever reported for the electrocyclization of heptatrienyl anions, and the first demonstration of catalysis for this type of electrocyclization.
- Mild and Catalytic Electrocyclizations of Heptatrienyl Anions.,
Arturo Orellana, Faizan Rasheed, Andrei Nikolaev, Anmol Dhesi, Tao Zeng, You Xuan Guo, Krishna Yarkali, Samira Komijani,
Chem. Sci. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC00926F