Test your knowledge! Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies chemical species by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It can be used with both magnetic sector and quadrupole systems.
A previous quiz explores its fundamental principles, while this one looks what information mass spectrometry can reveal about proteins.
 What is MALDI-TOF MS?
What is MALDI-TOF MS?
a) Microbial Assay Laser Diagnostics – Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
b) Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
c) Molecular Analysis Laser Diffraction – Technique of Focus Mass Spectrometry
Show the correct answer
Explanation: A mass spectrometry technique that ionizes proteins using a laser and measures their mass-to-charge ratio. It is widely used for rapid identification of proteins and microorganisms by analyzing their mass spectra.
 What is the main reason MALDI-TOF MS is preferred for protein analysis?
What is the main reason MALDI-TOF MS is preferred for protein analysis?
a) It fragments proteins into smaller ions.
b) It ionizes large biomolecules with minimal fragmentation.
c) It uses gas chromatography for separation.
d) It only detects small molecules.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: MALDI-TOF MS allows ionization of large biomolecules like proteins without significant fragmentation, preserving structural integrity.
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) is a specialized mass spectrometry technique ideal for analyzing large biomolecules such as proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids.
It works by embedding the sample in a light-absorbing matrix, which is then hit with a laser to ionize the molecules without fragmenting them. These ions are accelerated through a flight tube, and their time of flight is measured to determine their mass-to-charge ratio. MALDI-TOF is used in proteomics and for analyzing biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
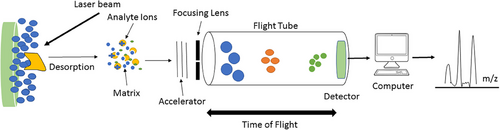
The basic principle of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Picture taken from [1]
 What is the primary clinical application of MALDI-TOF MS?
What is the primary clinical application of MALDI-TOF MS?
a) Measuring blood glucose levels.
b) Detecting viral RNA.
c) Identifying bacterial and fungal species.
d) Determining antibiotic resistance.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: In clinical microbiology, MALDI-TOF MS is primarily used to identify bacterial and fungal pathogens by analyzing their protein profiles. It is a game-changer for diagnostics due to its speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
 How does MALDI-TOF MS identify microorganisms?
How does MALDI-TOF MS identify microorganisms?
a) By comparing spectral data with a database of known organisms.
b) By visual inspection under a microscope.
c) By measuring the temperature of cultures.
d) By manual analysis of colony shape.
e) By measuring the microorganism’s electrical conductivity.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: MALDI-TOF MS identifies microorganisms by analyzing their unique protein mass spectra. These spectral fingerprints are matched against a reference database, allowing rapid and accurate identification of bacteria and fungi, often within minutes. Comparing to a reference database is fast because the mass spectra are digital fingerprints that can be rapidly matched by computer algorithms.
 Why is TOF MS particularly useful in proteomics?
Why is TOF MS particularly useful in proteomics?
a) It can analyze only inorganic compounds.
b) It provides high-resolution images of proteins.
c) It detects low concentrations of large biomolecules.
d) It uses chromatography for separation.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: TOF MS is highly sensitive and ideal for detecting low concentrations of proteins and peptides.
 Which type of laser is most commonly used in MALDI for protein ionization?
Which type of laser is most commonly used in MALDI for protein ionization?
a) Infrared laser.
b) Ultraviolet laser.
c) Far-infrared/Terahertz laser.
d) X-ray laser.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: UV lasers are preferred because they provide sufficient energy for ionization while minimizing fragmentation.
 In which types of biological samples can mass spectrometry-based methods be used to study lncRNAs? Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are RNA molecules that do not make proteins but help control how genes are turned on or off.
In which types of biological samples can mass spectrometry-based methods be used to study lncRNAs? Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are RNA molecules that do not make proteins but help control how genes are turned on or off.
a) Only blood samples.
b) Only plant tissues.
c) Only bacterial cultures
d) Complex biological samples such as cells, tissues, and bacterial cultures.
Show the correct answer
Explanation: MS-based approaches can be applied to a wide range of biological samples, including mammalian cells, tissues, and microbial cultures, for detecting and quantifying lncRNA-associated proteins or modifications.
MS works by detecting molecules based on their mass and charge, but it cannot see free RNA directly very well. In biological samples, lncRNAs are often bound to proteins or chemically modified, which makes them heavier and easier to ionize. When the sample is prepared, these RNA–protein complexes or modified RNAs can be vaporized and charged by the laser, and the mass spectrometer measures them. This is why lncRNAs can be studied in cells, tissues, or body fluids—because they exist there in forms that the instrument can detect.
Congratulations! You’ve just mastered a lot about MS—great job!
Source
Explore this Review to learn more about protein mass spectrometry:
 Mina Moradi, Zahra Farjami, Mohammad Mehdi Akbarin, Spectrometry and Its Application for the Detection of RNA-Binding Proteins: Advancements, Techniques and Challenges, Analytical Sciences Advances 2025. https://doi.org/10.1002/ansa.70026
Mina Moradi, Zahra Farjami, Mohammad Mehdi Akbarin, Spectrometry and Its Application for the Detection of RNA-Binding Proteins: Advancements, Techniques and Challenges, Analytical Sciences Advances 2025. https://doi.org/10.1002/ansa.70026
Also of Interest