Flow cytometry is essential for quantifying cellular heterogeneity in fields like immunology, cancer biology, and infectious disease monitoring but is often limited to labs due to its bulk, cost, and fragility. Sungyoung Choi, Hanyang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and colleagues have introduced a computational hyperspectral microflow cytometer (CHC) that accurately discriminates spectrally overlapping fluorophores labeling individual cells.
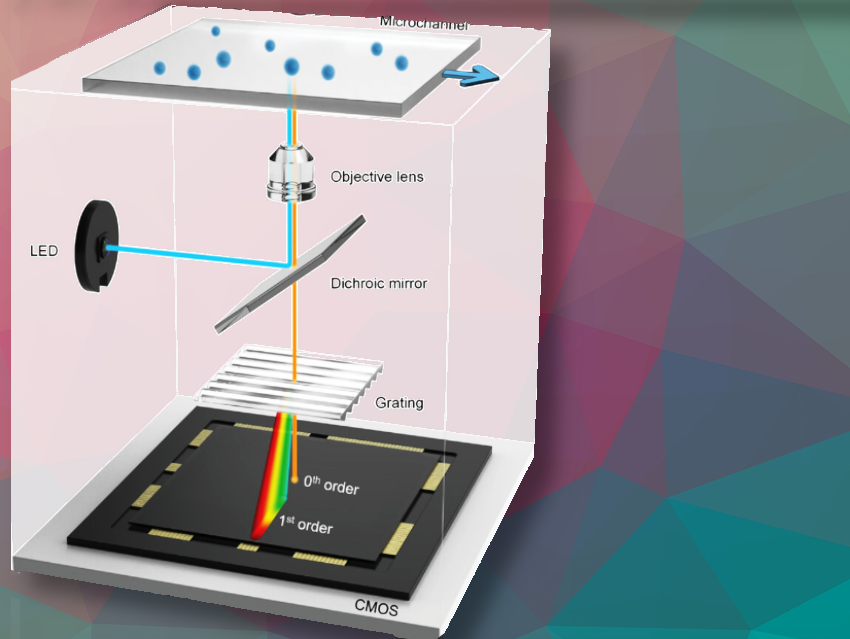
The CHC uses a dispersive optical element and an optimization algorithm to detect the full fluorescence emission spectrum of flowing cells with high spectral resolution (≈3 nm) in the range of 450 to 650 nm by reconstructing spectral information from diffracted fluorescence images of single cells. It includes a microfluidic device that ensures in-focus imaging through viscoelastic sheathless focusing, improving microflow cytometry analysis accuracy and reliability.
Cells labeled with fluorophores are aligned in a microfluidic channel to prevent overlap and pass sequentially through the interrogation region. The emitted fluorescence light is diffracted by a transmission grating, creating a characteristic intensity distribution that is captured by an image sensor. The CHC then uses an optimization algorithm to reconstruct the original spectrum from the diffracted images, ensuring high spectral resolution while maintaining spatial accuracy.
To demonstrate CHC’s spectroscopic capability, the team tested fluorescent particles with distinct or similar spectral characteristics and compared the results to those of a commercial spectrometer. Using three antibodies (anti-CD3, -CD4, and -CD8), they identified T lymphocyte subpopulations and tracked changes upon cell activation, highlighting CHC’s potential for immune cell monitoring.
Overall, CHC represents a significant breakthrough in microflow cytometry the reserchers say, and may facilitate its use for immune cell monitoring. The researchers suggest that CHC can be applied to various clinically significant cells, including stem cells and cancer cells, offering an accessible solution for multiplexed immunophenotyping even in resource-limited settings.
- Computational Hyperspectral Microflow Cytometry,
Hyo Geun Yun, Yoel Alonso Cadierno, Tae Won Kim, Arrate Muñoz-Barrutia, Daniel Garica-Gonzalez, Sungyoung Choi,
Small 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202400019