Janus kinase inhibitors, or JAK inhibitors, are immune-modulating drugs that inhibit the activity of one or more Janus kinase enzymes They can be used in the treatment of cancer or inflammatory diseases. The JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, for example, is an approved drug. However, like many anticancer drugs, it can have significant adverse effects. One approach to lessen these effects is the development of photoreleasable drugs, which are administered in a “caged” form with a light-removable protecting group. The active drug is then released upon irradiation with light at the desired time and location.
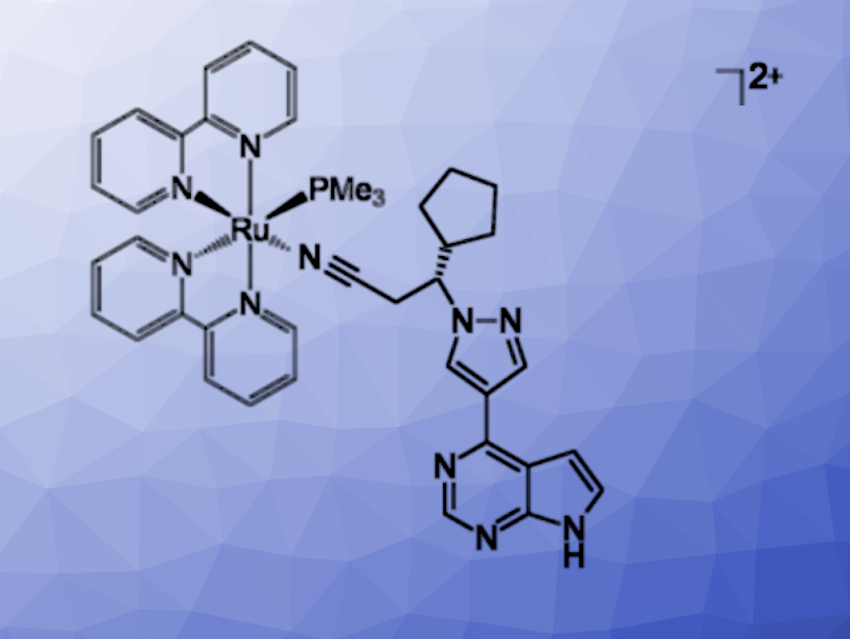
Roberto Etchenique, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina, and colleagues have developed the complex [Ru(bpy)2(PMe3)Ruxolitinib]2+ (RuBiRuxo, pictured; bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine), which can deliver the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib in a light-controlled manner. The complex dissociates under blue LED light and releases the active drug quickly and cleanly. It was prepared from [Ru(bpy)2(PMe3)(H2O)](CF3SO3)2 and ruxolitinib in methanol at 50 °C.
The team found that the complex is stable in the dark under physiological conditions. When irradiated with light, it is active against lymphoma cells in vitro and induces apoptosis (programmed cell death). The researchers also found evidence to confirm that the photorelease of ruxolitinib from RuBiRuxo influences the activity of Janus kinase enzymes. Overall, the approach could be useful, e.g., for the treatment of lymphomas that affect the skin.
- RuBi-Ruxolitinib: A Photoreleasable Antitumor JAK Inhibitor,
Estefania Rafic, Cindy Ma, Bobby B. Shih, Hannah Miller, Rafael Yuste, Teresa Palomero, Roberto Etchenique,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c01720