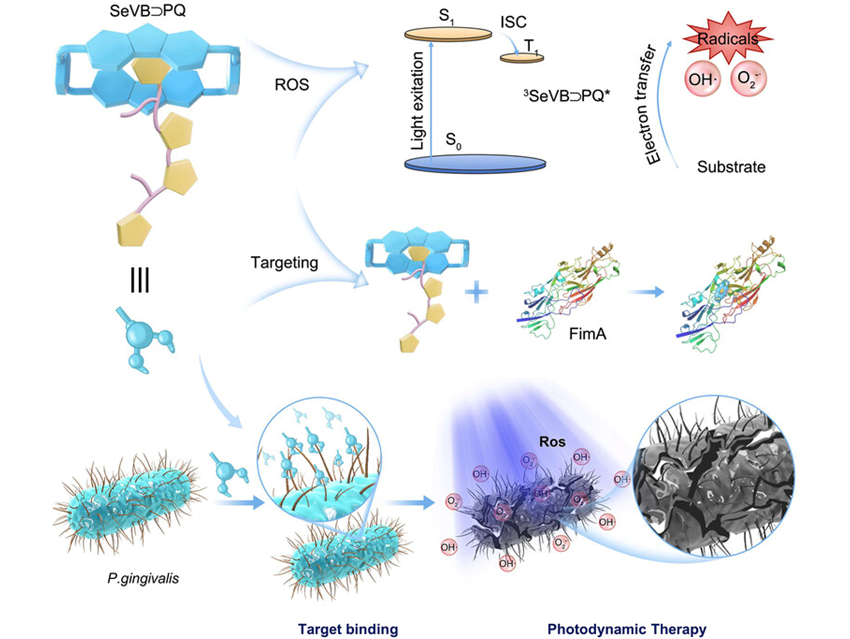
Gang He and Dandan Pei from Xi’an Jiaotong University, China, along with colleagues, have developed a targeted photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy (PDT) of periodontitis. Periodontitis, a biofilm-related infectious disease, can cause gum recession, tooth loss, and even exacerbate systemic conditions. Traditional treatments, such as scaling or antibiotics, are often limited by resistance, technical constraints, and unpredictable outcomes. PDT, which uses light-activated photosensitizers to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), offers a minimally invasive and resistance-free alternative.
The team designed SeVB⊃PQ, a supramolecular complex combining a selenium-containing viologen (=bipyridinium derivative) cyclophane (SeVB) with a targeting peptide (PQ) that specifically recognizes Porphyromonas gingivalis, a key periodontal pathogen. This smart design enables precise bacterial targeting and efficient ROS generation directly at the infection site. Laboratory and animal studies showed that SeVB⊃PQ significantly outperformed both its precursor molecule and the clinical photosensitizer methylene blue. It effectively killed P. gingivalis, reduced plaque, protected alveolar bone, and helped restore a healthy subgingival microbiome.
This study establishes a new paradigm for designing targeted photosensitizers, offering an efficient and safe therapeutic approach for periodontitis and providing valuable insights for developing precision therapies against other specific pathogenic infections in the future.
- Fimbriae-Targeted Peptide-Selenoviologen Cyclophane Complex for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy of Periodontitis,
Rui Ding, Yawen Li, Yuchen Zhang, Qi Sun, Ang Li, Kun Zhou, Dandan Pei, Gang He,
Aggregate 2025
https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70159