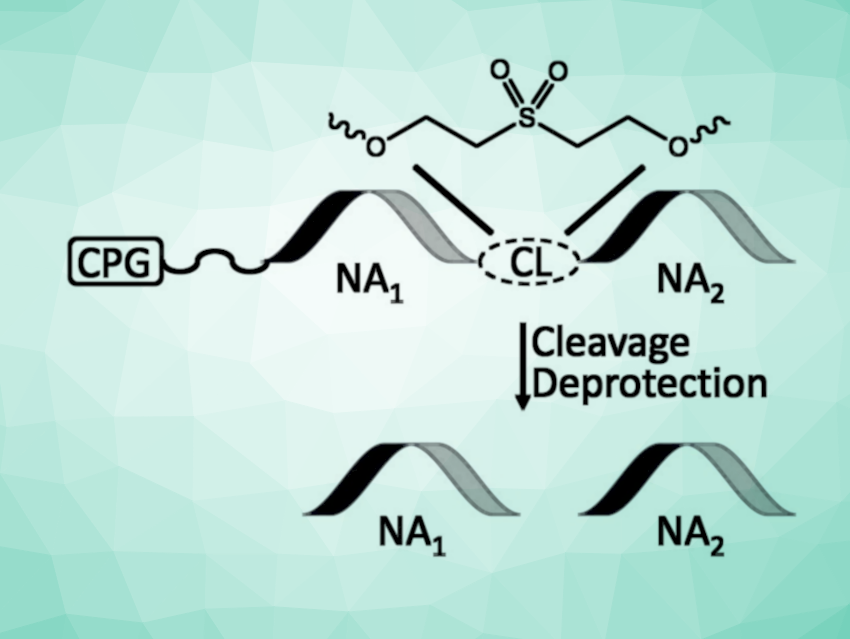
The preparation of oligonucleotides is important in research and (bio)technology. Tandem oligonucleotide synthesis (TOS) is an attractive strategy to increase the production throughput while lowering costs. In TOS, multiple oligonucleotides are prepared in a single sequence, separated by cleavable linkers, using solid-phase synthesis. The linkers are then cleaved to release the desired oligonucleotides. TOS can increase production, uses less support material, minimizes handling steps, and can also be used to synthesize multiple copies of the same oligomer. Existing TOS approaches can have drawbacks such as a need for harsh conditions to cleave the linkers and most often focus on DNA synthesis, despite the importance of RNA in research.
Derek K. O’Flaherty, University of Guelph, Canada, and colleagues have found that a commercially available building block can be used to perform TOS efficiently, leading to a simple and general tandem oligonucleotide synthesis method for DNA and RNA. The team used a 2,2′-sulfonyldiethylene linker (pictured, CL = cleavable linker), which is typically employed to phosphorylate the terminal positions of synthetic nucleic acids. This linker is cleaved during the standard deprotection of DNA and RNA, and can, thus, be used for efficient TOS processes with no modifications to the standard operating protocols.
The resulting oligomers containing terminal phosphate groups can further be transformed into useful chemically modified derivatives. The team points out that in contrast to other TOS methodologies that typically require the preparation of custom building blocks, the developed approach could be accessible to a broad range of research groups, including those lacking organic synthesis infrastructure.
- A facile and general tandem oligonucleotide synthesis methodology for DNA and RNA,
Jagandeep S. Saraya, Derek O’Flaherty,
ChemBioChem 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202300870